Jute Scouring Process: A Complete Easy Guide for Beginner
Introduction
Jute is a natural bast fiber. It is used for making sacks, ropes, mats, geotextiles, and decorative fabrics. However, raw jute contains impurities like as oil, wax, dust, pectin, and lignin. These impurities make the jute fiber stiff and dull. Hence, the Jute scouring process is carried out to remove these impurities. The jute scouring process removes natural impurities and improves the fiber’s absorbency as well as its softness. This article is about jute scouring process with recipe calculation.
What is jute scouring?
Jute scouring is a chemical cleaning process used to remove impurities from raw jute fiber. Raw jute fiber boil in an alkaline solution, which helps eliminate oily and gummy substances.
Objectives of Jute Scouring
- Jute scouring process removes natural impurities such as oil, wax, and pectin.
- It also eliminates dirt and dust from the fiber surface.
- It also improves hydrophilicity (water absorption).
- Besides, Jute scouring increases the whiteness and softness of the fiber.
You may read: Cotton Pigment Dyeing Process: Explained in 3 Easy Steps
Chemical composition of Raw Jute
| Component | Amount (Approx. %) |
| Cellulose | 65.2% |
| Hemi-cellulose | 22.2% |
| Lignin | 10.8% |
| Waxes, fats, pectin, other | 0.3% |
N.B.: The main objects of scouring stage to remove waxes, fats, and pectin.
Jute Scouring Recipe
Jute fiber has good resistance to alkalis. But it is easily attacked by hot dilute or cold concentrated material acids. Thus, jute scouring is done with alkali treatment. The following recipe is used for jute scouring process.
| Chemical | Amount |
| Wetting agent | 1.0-2 gm/l |
| Detergent | 0.5-1.0 gm/l |
| Sequestering agent | 1.0-2.0 gm/l |
| Caustic soda | 0.5-1.0 gm/l |
| Soda ash | 3.0-5.0gm/l |
| Temperature | 90-950 C |
| Time | 45-60 min |
| pH | 10.5±0.5 |
| M:L | 1:30 |
Recipe Calculation
- Total amount of liquor= 5×30= 150 ml
- Required wetting agent= {total amount of liquor× recipe amount (gm/l)} ÷ (1000×stock solution) = (100×2) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 10 ml [Stock solution 2%]
- Required Detergent = (100×1) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 5 ml
- Require Sequestering agent= (100×2) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 10 ml
- Require Caustic soda= (100×1) ÷ (1000× 2%)= 5 ml
- Required soda ash= (100×5) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 25 ml
- Required water= {150- (10+5+10+5+25)}= 95 ml
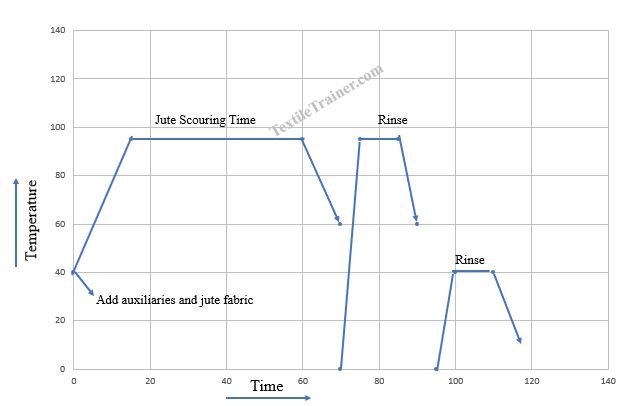
Jute Scouring Process Curve
Jute Scouring Procedure
The jute scouring process is simple and follows few steps. Following the steps of the jute scouring.
- Initially, wetting agent, detergent, and sequestering agent are added to the bath at room temperature.
- After a few minutes, alkalis are added and the temperature to 90-950 C @20C/min.
- Next step, machine is run for 60 minutes.
- Subsequently, drop the liquor after 60 minutes.
- Now, jute fabric is rinsed twice with hot and cold water successively.
Jute Scoured Sample

FAQ on Jute Scouring
- What is the benefits of jute scouring?
- Jute scouring removes dust, wax, and oil from jute fabric.
- It improves fiber softness and absorbency.
- It enhances the color brightness of jute fabric.
- Which chemical is commonly used in jute scouring?
- Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3) is commonly used for jute scouring.
- What temperature is used for jute scouring?
- Generally 90–95 °C for 1–2 hours is used for jute scouring.
- Can jute be scoured and bleached together?
- Yes, it is possible combined scouring and bleaching of jute fabric. In combined processes, hydrogen peroxide is used for simultaneous scouring and bleaching.
- What happens if jute is not properly scoured?
- The fiber remains stiff and non-absorbent. Hence, uneven dyeing and poor finishing appear.
Conclusion
The jute scouring is a crucial pre-treatment process. This process increases the quality, softness, as well as dyeability of jute fibers and fabrics. But, it is an important to control alkali concentration perfectly.