Vat dyeing process for Cotton Fabric: Step-by-step Guide
Introduction
Vat dyeing is a popular used dyeing method for coloring cellulosic fiber specially cotton fabric. This article is brief the vat dyeing process for cotton with typical recipe and recipe calculation. Vat dye is the most popular dyeing owing to its high colorfastness on cellulosic fiber. However, it is an expensive class of dyes compared to other dyes used for cotton fabric. Vat dye is an insoluble dye and it has no much affinity for cotton fabric. It must be converted to solubilized before dyeing by using caustic and hydroz. This solubilized state of vat dye is called “leuco” form of vat dye. Leuco vat dye has an affinity to the fiber. After exhaustion of leuco vat dye, it is oxidized to form insoluble dye and locks inside the fiber.
What is Vatting?
Vatting is an important step in the vat dyeing process, in which the insoluble vat is converted into a soluble form known as the “ leuco” form of the dye. In the vatting process, an alkali and a reducing agent are used as reducing agents to convert insoluble to soluble conditions. However, soluble leuco vat dye easily penetrates into the cotton fiber and then, oxidizes to form insoluble colored pigment again inside the fiber.
You can read: Biopolishing of Cotton: Benefits & Impact on Fabric Quality
Properties of Vat dye
- Vat dye is a water-insoluble dye. It can not be applied directly to textile goods.
- Vat dye is ideal for cellulosic fiber specially, for cotton, viscose, and linen.
- It has poor affinity for protein fibers like wool, silk.
- The vat dyeing process is difficult and involve multi-step.
- It has excellent colorfastness to washing, and light, but, poor colorfastness to rubbing.
- It is costly.
Classification of vat dye
- Basis on the chemical structure
- Anthraquinonoid vat dye
- Indigoid vat dye
- Basis on application
- IN (Indanthrene normal)
- IW (Indanthrene warm)
- IK (Indanthrene cold)
Trade of vat dye
| Trade Name | Company Name | Country |
| Navilon | Indian Dyestuff Industries Ltd. | Indian |
| Suprasthen | Associated Dyestuff Industries | Indian |
| Reoline | M.K. Soorenji and Co. | Indian |
| Indrathene | Badische Aniline and Soda Fabriek A.G | Germany |
| Anthra | Badische Aniline and Soda Fabriek A.G | Germany |
| Indathren | Farbenfabriken Bayer A.G. | Germany |
| Helindon | Farbenfabriken Bayer A.G. | Germany |
| Cibanone | Ciba-Geigy A.G. | Switzerland |
| Ciba | Ciba-Geigy A.G. | Switzerland |
| Mikanthrene | Mistsui Chemical Industry Co. Ltd. | Japan |
| Calconoid | American Cyanamid Co. Dyes Dept. | U.S.A |
Mechanism of Vat dye
Generally, vat dyeing process is carried out in two subsequent step (vatting and dyeing). But, the whole vat dyeing process consists of server steps such as:
Vatting (Reduction)
Vat dye is an insoluble dye. A vatting process transforms an insoluble dye into its soluble form. Initially, vat dye is treated with strong reducing agent (Hydroze) in the presence of caustic soda. Hence, insoluble vat dye becomes a soluble form. This soluble form of vat dye is known as “ Leuco vat dye.”
Dyeing
Textile fiber has no affinity to vat dye but has an affinity to leuco vat dye. After vatting process, soluble vat dye is poured into the dye with other auxiliaries. Vatting temperature and dyeing temperature depend on the dye class.
| Dye class | Process Temp (0) | Add reagent (gm/l) | |||
| Vatting | Dyeing | Caustic | Hydroze | Salt | |
| IN | 50-60 | 60-70 | 5.0-12.0 | 4.0-8.0 | × |
| IW | 50 | 40-50 | 2.0-6.0 | 1.0-4.0 | 3.0-5.0 |
| IK | 50 | 20-30 | 1.0-4.0 | 0.5-3.0 | 5.0-15.0 |
Oxidation
In the time of dyeing, reduced vat dye molecules are penetrated into the fiber. But, they do not make any bond. Then, exhausted dye molecules are oxidized and converted back into insoluble form. As a result, dye molecules become fixed within the fiber.
After treatment
Finally, the dyed fabric is treated with soap to remove unfixed dye from the surface of the fiber. Then, the fabric is neutralized by using acetic acid.
Typical Recipe for Vat Dyeing Process
| Chemical | Amount (gm/l) |
| Wetting agent | 0.5-1.0 |
| Sequestering agent | 1.0-2.0 |
| Dispersing agent | 1.0-2.0 |
| Salt | 5.0-10.0 |
| Caustic soda | 5.0-12.0 (according to vender recommendation) |
| Hydroz (Sodium hydrosulfite) | 4.0-8.0 (according to vender recommendation) |
| Dyestuff | 2% |
| Temperature | 60-700 |
| Time | 40-50 min |
| M:L | 1:20 |
| Cotton fabric weight | 5 gm |
Recipe calculation
For dyeing recipe calculation following two formulas is used.
- Required auxiliary= (Total amount of liquor× recipe amount) ÷ (1000× stock solution)
- Required dyestuff= (Fabric weight × Shade percentage) ÷ Stock solution
Now, Let’s calculate the dyeing recipe according to the above-mentioned recipe for vat dye
- Total amount of liquor required for vat dyeing= 5×20= 100 ml
- Wetting agent required= {total amount of liquor× recipe amount (gm/l)} ÷ (1000×stock solution) = (100×1) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 5 ml [ use 2% stock solution]
- Sequestering agent required= (100×2) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 10 ml [ use 2% stock solution]
- Required dispersing agent= (100×2) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 10 ml [ use 2% stock solution]
- Require salt= (100×10) ÷ 1000 = 1 gm [ No need stock solution as we will take it solid form]
- Required caustic soda = (100×12) ÷ 1000 = 1.2 gm [ No need stock solution as we will take it solid form]
- Required hydroz = (100×8) ÷ 1000 = 0.8 gm [ No need stock solution as we will take it solid form]
- Required dyestuff= (5× 2%)÷ 1%= 10 ml [ use 1% stock solution]
- Required water= {100- (5+10+10+10)}= 65 ml
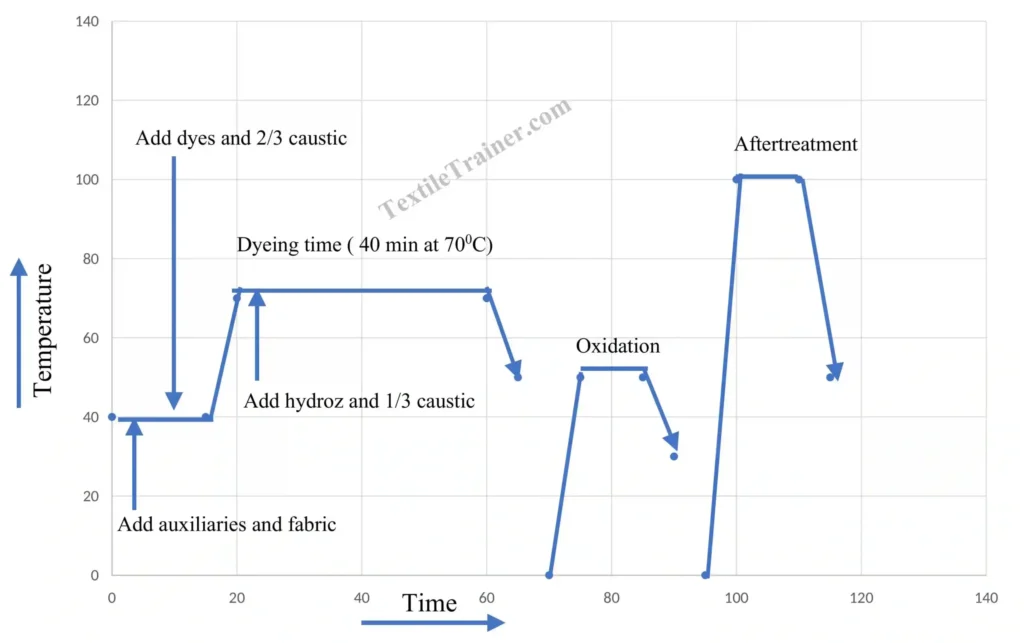
Process curve
Procedure
Dyeing
- Initially, set the dye bath at 400 C and add auxiliaries except for hydroz and caustic soda. Load the fabric to the machine. Next, operate the machine for 5 to 10 minutes
- Now, add dye according to the recipe calculation and run the machine for 5 minutes.
- Add two-thirds (2/3) of the caustic soda and continue running the machine for 5 minutes.
- Rise the temperature to 60-700C @ 2-30 C/ minute and run for 5 minutes.
- Add sodium hydrosulfite (hydroz) to the bath along with remaining one-third( 1/3) of caustic soda.
- Continue running the dye bath for 40 to 50 minutes, maintaining the reduction condition by checking with vat reduction paper.
- Now, rise the fabric to remove unfix dyestuff.
Oxidation
After dyeing, oxidation process is done. The oxidation process transforms the soluble leuco vat dye back into its insoluble form. Generally, oxidation process can be done by using oxidizing agent. Hydrogen peroxide (35%) used as a oxidizing agent. For oxidation, 0.5-1.0 gm/l Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is used at 30-500 for 10 minutes.
Aftertreatment
Aftertreatment or soaping process is done to remove unfix dye from the surface of the fabric. For soaping process, detergent ( 1.0-2.0 gm/l),and Soda ash (1.0-2.0 gm/l) are used at 95-1000 C for 10-15 min. subsequently, rise the fabric with cold-hot-cold water respectively. Next, sometimes softening agent is use for good hand feel but it is optional process. Finally, dry the fabric.
References
- Hossain, M. F. (2015). Practice of Textile Coloration, Volume-I. Dhaka: Books Fair Publications.
- Hossain, M. S. (2014). Introduction to Textile Engineering. Dhaka: Books Fair Publications.
- Kabir, D. S. (2016). Chemistry of Dyes & Pigments. Dhaka: Books Fair Publications.
- Vankar, P. S. (2017). Natural Dyes for Texiltes (Sources, Chemistry and Applications). United Kingdom: WoodHead Publication.



