Sulfur Dyeing Process in Textile: Step-by-Step Guide for Cotton
Introduction
Nowadays sulfur dyeing process is declining day by day owing to environmental issue. Sulfur is sensitive to the environment. Though it has problems but it is very popular dye for black share still now. For black shade, sulfur dyes are one of the most widely used dyestuffs in the textile industry, especially for cotton and other cellulosic fibers. However, this article will explain the complete sulfur dyeing process in textile (cotton fabric) , additionally its properties, mechanism, dyeing recipe, recipe calculation, advantages of sulfur dye as well as disadvantages of sulfur dye. Initially, let’s learn what sulfur dye is.
What is Sulfur Dyes?
Sulfur dyes are insoluble dyes containing sulfur linkages, i.e. sulfide (-S-), disulfide (-S-S-), polysulfide (-Sn -) links as well as heterocyclic rings. It has been suggested that some sulfur dyes are based on the phenothiazonethioanthrone chromophoric system. In their original form, they cannot dissolve in water. Hence, they are converted into a soluble form called as leuco sulfur by treating with reducing agent as sodium sulfide (Na2S), before dyeing. After dyeing, the fabric is oxidized to revert the dye to its insoluble form.

Sulfur Dyes Properties
Some important properties of Sulfur dyes are given below:
- Sulfur dyes are suitable for cellulosic fibers like cotton, linen, and viscose.
- It is cheap and uses are easy.
- Sulfur dyes are water-insoluble dye. Before dyeing, these dyes have to be converted into water-soluble (leuco form). After dyeing, it will be oxidized and converted into insoluble sulfur dye.
- It makes a colloidal solution like a direct dye.
- Moreover, its wet fastness is good, but light fastness is moderate.
- Additionally, it is suitable for dark shade, not for light shade.
Mechanism of Sulfur dye
The mechanism of sulfur dye is divided into three steps. They are:
- Reduction
- Absorption
- Oxidation
Step-1: Reduction
Sulfur dye is insoluble dye. Initially, sulfur dye is reduced in an alkaline bath containing sodium sulfide and soda ash. Hence, sulfur linkage (-S-S-) breaks to form leuco sulfur dye. Leco sulfur dye is water-soluble.
- D-S-S-D + 2[H] = D-SH + HS-D ( soluble leuco sulfur dye)
Step-2: Absorption
Now, the soluble leuco form of sulfur dye diffuses into the amorphous region of cellulose fiber. It creates weak hydrogen and van der waals bonds.
Step-3: oxidation
After dyeing, the fabric is oxidized to covert leuco sulfur dye back to insoluble sulfur dye. Hence, dye fixed in the fiber permanently.
- 2D-SH + HS-D + [O] = D-S-S-D (insoluble) + H2O
Sulfur Dye Recipe
A typical recipe for sulfur dye process for cotton fabric is given below:
| S/N | Chemical | Amount |
| 1. | Wetting agent | 0.5-1.0 gm/l |
| 2. | Sequestering agent | 1.0-2.0 gm/l |
| 3. | Sulfur dye | 2% |
| 4. | Sodium sulfide (Na2S) | 3-6 gm/l |
| 5. | Salt (glauber/ common) | 10-20 gm/l |
| 6. | Soda ash | 1-3 gm/l |
| 7. | Temperature | 90-1000 C |
| 8. | Time | 60 min |
| 9. | M:L | 1:20 |
| 10. | Sample weight | 5 gm |
Recipe calculation:
Recipe calculation for sulfur dyeing process for cotton fabric is below. For dyeing recipe calculation following two formulas is used.
- Required auxiliary= (Total amount of liquor× recipe amount) ÷ (1000× stock solution)
- Required dyestuff= (Fabric weight × Shade percentage) ÷ Stock solution
Now, Let’s calculate the dyeing recipe for sulfur dyeing process for cotton fabric.
- Total amount of liquor required for sulfur dyeing process= 5×20= 100 ml
- Wetting agent required= {total amount of liquor× recipe amount (gm/l)} ÷ (1000×stock solution) = (100×1) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 5 ml [ use 2% stock solution]
- Sequestering agent required= (100×2) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 10 ml [ use 2% stock solution]
- Required Sodium sulfide = (100×6) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 30 ml [ use 2% stock solution]
- Require salt= (100×20) ÷ 1000 = 2 gm [ No need stock solution as we will take it solid form]
- Required soda ash = (100×3) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 15 ml [use 2% stock solution]
- Required dyestuff= (5× 2%)÷ 1%= 10 ml [ use 1% stock solution]
- Required water= {100- (5+10+30+15+10)}= 30 ml
Sulfur Dyeing Process Curve
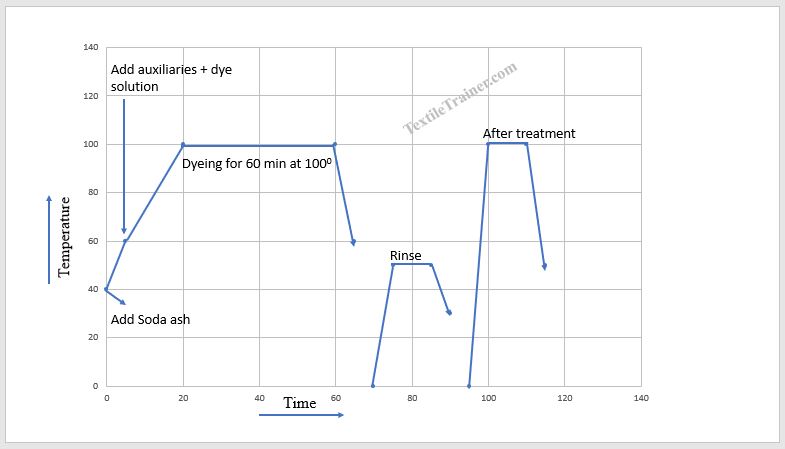
Sulfur Dyeing Process
Step-1: Reduction
- Initially, the dye solution is prepared. Dye paste is made by adding a wetting agent, sodium sulfide, and a small amount of hot water to the dyestuff.
- Now, add enough (20 times of dye amount) hot water to the dye paste and boil it for 10-15 minutes. Now, insoluble sulfur dye has become soluble.
Step-2: Dyeing
- Then, prepare the dyebath with substrate at room temperature.
- Subsequently, add the necessary amount of soda ash and raise the temperature to 600 C. Then, add the prepared dye solution into the dyebath and raise the temperature to 900 C.Now, add the required amount of salt to the dyebath.Run the machine at 90-1000 C for 60 min.Next, cool down the bath and drop.
- Aftertreatment: To improve colorfastness properties, the sample is treated with potassium dichromate (0.5-1.0 gm/l), copper sulfate (1.0-2.0 gm/l), and acetic acid (1-3.0 gm/l) at 70-750C for 10-15 minutes.
Step-3: Oxidation
- After dyeing, sulfur-dyed fabric must be oxidized to convert the soluble form to an insoluble form. In the oxidation process, sulfur dyed fabric is treated with hydrogen peroxide (1.0-2.0 gm/l) at 600C for 15-20 min.
- Now, rinse the sample with fresh water.
- Finally, dried the sample in the oven.
Advantages of sulfur dye
- The sulfur dyeing process is cost-effective for deep shades.
- The wash fastness of sulfur dye is high, but light fastness is fair to good.
- Simple application process.
- Low energy is required.
- Resistance of the chemical of sulfur dye is moderate to good.
Disadvantages of sulfur dye
- Sulfur dye generates sulfide effluent which pollutes the environment.
- It can damage fibers if sodium sulfide is excessive.
- Limited shade.
FAQ
- What is the main reducing agent used in sulfur dyeing?
- Answer: The main reducing agent is sodium sulfide (Na₂S). sodium sulfide (Na₂S) converts the insoluble sulfur dye into its soluble leuco form.
- what happens during the oxidation step?
- Answer: During oxidation, the soluble leuco sulfur dye is converted back to its insoluble sulfur dye. Hence, the dye fix with fiber permanently.
- what are the limitations of sulfur dyes?
- Sulfur dye release harmful sulfide effluent which impact on environment.
- Additionally, it is not suitable for bright colors or synthetic fibers.
- what is the chemical form of leuco sulfur dye?
- Answer: The leuco form contains thiol groups (-SH) formed by breaking disulfide bonds (-S-S-). It is soluble in alkaline solution and easily absorbed by cotton.
- How can we improve the fastness properties?
- Answer: To improve the fastness properties of sulfur dyed fabric, the sample needs to be treated with potassium dichromate (0.5-1.0 gm/l), copper sulfate (1.0-2.0 gm/l), and acetic acid (1-3.0 gm/l) at 70-750C for 10-15 minutes.
Conclusion
The sulfur dyeing process for cotton fabric is an economical method. It helps to produce deep, durable shades on fabric. However, understanding the mechanism of sulfur dye and dyeing process on cotton fabric will help textile learn in the future or in their job life in the textile industry.
You may read:



