Biopolishing of Cotton: Benefits & Impact on Fabric Quality
Introduction
In today’s textile industry, the demand for high-quality, smooth, and durable cotton fabric is dramatically escalating day by day. Buyers are always searching for good quality products with good finishing properties. Biopolishing is one kinds of enzymatic finishing process that meet the buyer’s requirements. This cotton enzymatic process removes the protruding fibers from the surface of the fabric, resulting softer, and more refined look. However, this article will discuss the biopolishing of cotton with advantages and disadvantages. Here, present a recipe and recipe calculation for the cotton biopolishing process. But, what is biopolishing? Let’s know about it.
What is Biopolishing?
Biopolishing is a textile enzymatic finishing process that removes loose fiber, and protruding fibers from the surface of cotton fabric by using cellulase enzymes. Basically, loose fiber and protruding fibers are responsible for pilling on surface of fabric. Biopolishing process is widely used in the textile industry as a finishing process. Generally, this enzymatic finishing process used for:
- knitwear like T-shirts, and sportswear.
- casual and export garments.
Recipe for biopolishing process
| Chemicals | Amount (gm/L) |
| Acetic acid | 0.5-2 |
| Enzyme | 1-2 |
| Temperature | 60-700 C (depending on vendor recommendation) |
| Time | 10-15 mins |
| pH | 4-5 |
| M:L | 1:20 |
| Sample weight | 5 gm |
Recipe calculation
- Total amount of liquor= 5×20= 100 ml
- Required acetic acid= {total amount of liquor× recipe amount (gm/l)} ÷ (1000×stock solution) = (100×2) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 10 ml
- Required enzyme= (100×2) ÷ (1000× 2%) = 10 ml
- Required water= {100- (10+10+)}= 80 ml
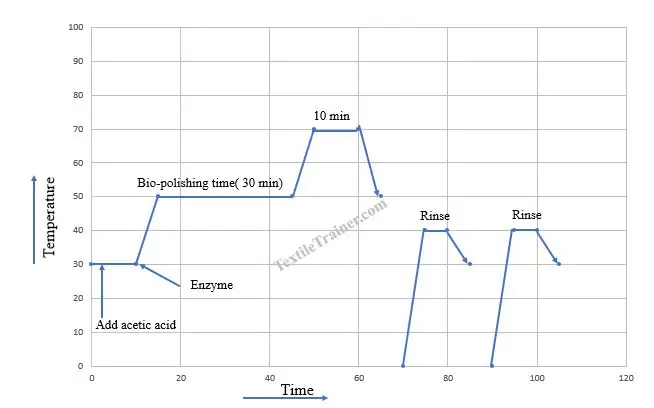
Biopolishing Process Curve
Biopolishing Procedure
- Set the bath with substrate at room temperature and add the required amount of acetic acid to maintain a pH 4-5.
- Run the machine for 5-10 minutes and add the enzyme.
- Now, Raise the temperature to 500 C and run the machine for about 15-25 minutes.
- After 15-25 minutes, raise the temperature to 60-700 C for 10-20 minutes.
- Lower the temperature to 500C and drop the bath.
- Rinse the fabric 2 times.
- Carry the subsequent process.
Result

Impact on Fabric Quality
- The biopolishing process removes the loose fiber from the surface of the fabric that is responsible for pills.
- This process creates a uniform surface as well as a cleaner surface.
- Enzymatic biopolishing increases the hand feel which is a key requirement of buyers.
- It also improves the appearance of the fabric after dyeing.
Limitations of biopolishing cotton
- Enzymes are comparatively more expensive than traditional chemicals.
- Sometimes enzymes reduce the fabric strength.
- Enzyme parameters should be monitored carefully to avoid fabric damage.
FAQs
1. What is biopolishing in cotton fabric?
Biopolishing is an enzymatic finishing process especially used for cotton knit fabric to remove loose fiber as well as the protruding fiber from the surface of a cotton knit fabric. Resulting of biopolishing is smoothness, softness, reduced pilling, and increased overall appearance and hand feel of the fabric.
2. What enzymes are used in biopolishing?
The most popular enzymes used for biopolishing is cellulases. Cellulases enzyme break down the cellulose fibers on the surface of the fabric without affecting the basic structure and strength of the fabric.
3. Is biopolishing safe for the environment?
Yes, the biopolishing process is considered an eco-friendly process. In the cotton biopolishing process uses biodegradable enzymes instead of harmful chemicals. This process consumes less water and energy.
4. Does biopolishing affect the strength of cotton fabric?
Yes, if don’t do this process the proper way, it may cause reduced fabric strength. But, if done correctly under controlled parameters, biopolishing does not affect the strength of fabric.
References
- Belal, P. D. (2016). Understanding Textiles for a Merchandiser. Dhaka: L.B Graphics and Pringing.
- Chawla, K. (1998). Fibrous Materials. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press.
- Hossain, M. F. (2015). Practice of Textile Coloration, Volume-I. Dhaka: Books Fair Publications.
You May Read