Name of the Experiment:
Study on single yarn strength tester/ Lab report on determination of single yarn strength.
Introduction:
The importance of yarn strength is to be studied from several aspects depending on its end use. The textile materials show marked differences in strength among themselves. There are many factors that are to be considered while estimating the yarn strength. Yarns are used for manufacturing sewing threads and tough industrial fabrics. The end use of yarns depends upon the most important property, namely strength. However, the strength is not a single important property. Depending on the material’s end use, yarns can be prepared to meet the specifications. The strength property of spun yarn is usually combined with the twist technology and its relationship. However, there are various other factors that are to be considered, which will also influence the strength and its determination. While considering the yarns spun from staple fibers like cotton, viscose, etc., many inherent characteristics of known properties which influence the fiber strength of the said yarn are important.
Objectives:
- To know about strength of yarn.
- Come to learn pendulum type strength tester.
- To know working procedure of strength tester.
Principle of tensile testing machine:
- Constant rate of loading (CRL).
- Constant rate of extension (CRE).
In this experiment, we will use the pendulum lever principle with constant rate of traverse to measure the single yarn strength test.
A motor-driven pendulum strength tester, it is composed of an arm that pivots on ball bearings and has a quadrant at the top. The arm is attached to an upper clamp by a chain that passes over the quadrant and fixes it to the upper clamp. By clamping the specimen, the pulling force transfers to the pendulum, which, in turn, displaces the weight proportionally to its magnitude, which can be seen on the quadrant scale. It has two ranges: a lower scale and a higher scale. The lower scale is used when the pendulum is carrying a small weight. The higher scale is used when the pendulum is carrying more weight. The lower jaw is carried by a rack which is connected by a screw rod connected to a driving mechanism consisting of a clutch and declutch arrangement. A rod which carries the lower jaw can be changed of different length so that different length specimens can be tested in the tester. The specimen shall break within 20±3 seconds. The rate of traverse of the bottom jaw is 300±15 mm/min (12in per min).
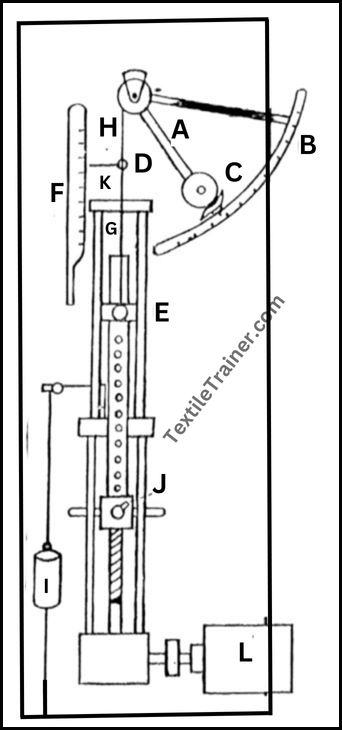
| A= Pendulum | B= Quadrant Scale |
| C= Pawl | D= Top Clamp |
| E= Bottom Clamp | F= Elongation |
| G= Yarn Sample | H= Steel Tape |
| I= Dead Weight | J= Clutch |
| K= Pointer | L= Motor |
Working procedure(Single Yarn Strength Tester):
There is a catch to arrest the pendulum, as well as the upper clamp movement. A material to be tested is clamped between the upper and lower clamps. The excess material is cut off exactly at the clamp position, and the catches are removed. When the machine is started, the lower jaw traverses downwards, imposing tension on the specimen and pulling the upper clamp, thus moving the pendulum over the quadrant scale. In order to maintain the pendulum arm’s position when the specimen ruptures, the pendulum arm is attached to a set of pawls on the serrated portion of the quadrant. The position of the pendulum arm gives the specimen’s breaking load. 5 tests are done in same way and calculate average breaking load. We can calculate tenacity in gm per tex by using below formula.
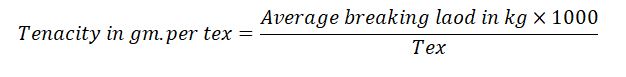
Conclusion:
In this experiment, we learned the principle of tensile testing machines. We also learned how to measure the strength of single yarn by using the single yarn strength tester. We thanked our teacher for giving us the opportunity to do this experiment. This experiment will be helpful for us in our future carrier.
More Lab Report:






I also think hence, perfectly indited post! .
As a Newbie, I am always searching online for articles that can help me. Thank you
Thnx….please share my article….