Most 25 Yarn Winding Defects and Remedies / Effective Solution
Introduction:
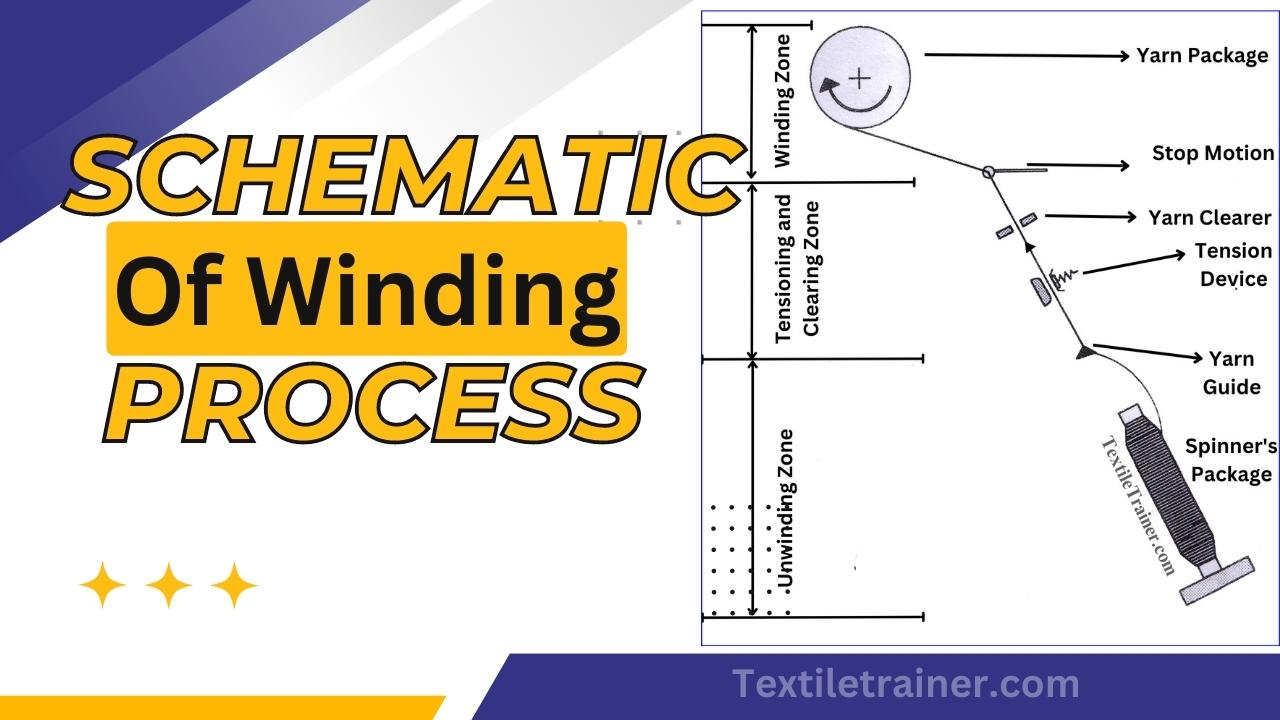
This article is about yarn winding defects with proper solution in effective way. In fabric manufacturing, yarn winding plays a crucial role in determining the quality and efficiency of the final product. Precision and attention to detail are required to achieve consistent and reliable results. During the subsequent stages of yarn processing, yarn winding facilitates the handling of yarn by transferring it from larger packages to smaller ones. A primary goal of yarn winding is to ensure uniform tension throughout the yarn.
During weaving or knitting, this is critical for maintaining the integrity of the yarn and preventing breakages or snags. As the yarn is wound onto the smaller packages, the tensioning devices on the winding machine play a vital role in maintaining tension. By minimizing variations in yarn thickness and ensuring even distribution of the yarn on the packages, proper tensioning contributes to the overall quality of the fabric.
In addition to tension control, yarn winding improves the appearance of finished fabrics by eliminating defects. Any damaged or defective yarn sections can be detected and removed during the winding process, such as knots, slubs, and excessive twists. Assuring that high-quality yarn is used in fabric production, winding machines are closely monitored by operators to identify and address these issues promptly. The winding of yarn also facilitates the handling and storage of yarn efficiently. Pirns and cheeses are smaller and easier to manage and store in an organized manner than larger packages. In addition, this optimizes the use of space in the manufacturing facility by facilitating the flow of materials.
Moreover, yarn winding plays an important role in increasing the productivity of fabric manufacturing. When yarn is prepared in smaller, ready-to-use packages, subsequent weaving or knitting machines can run smoothly without interruptions caused by having to change larger supply packages. By reducing downtime, improving workflow, and increasing production output, downtime is reduced.
List of Yarn Winding Defects
| Yarn winding defects | Yarn winding defects |
| 1. Yarn breakage | 14. Uneven winding |
| 2. Yarn slippage | 15. Yarn tangling or knotting |
| 3. Stitch | 16. Chaffed yarn |
| 4. Soft package | 17. Collapsed cone |
| 5. Bell-shaped cone | 18. The faulty shape of the package |
| 6. Formation of ribbon | 19. Tight bobbin |
| 7. Imperfect winding speed | 20. Wild yarn |
| 8. Mixing of different linear densities yarn | 21. Two end winding |
| 9. Nose bulging | 22. Ring-shaped cone |
| 10. Patches formation on the yarn | 23. Excessive full bobbin |
| 11. Slack knots | 24. Less removal of loose fibers, neps, slubs |
| 12. Overlapping | 25. Variation of tension |
| 13. Excessive full bobbin |
Yarn winding defects and remedies
The purpose of this article is to present the most common and important winding defects and how to solve them. These are the details that are given below:
1. Yarn Breakage:
Yarn breakage occurs when yarns break during the fabric manufacturing process. These issues can occur at various stages, such as winding, warping, weaving, or knitting, and can negatively impact the final fabric’s quality. To improve production efficiency, it is critical to understand and address the causes of yarn breakage. The following are some common causes of yarn breakage:
Causes of the defect:
- A yarn with inherent defects, such as weak spots, knots, or uneven thickness, is more likely to break
- When the yarn is put under excessive mechanical stress or strain during processing, it can break.
- The yarn can be overstressed by sharp edges, rough surfaces, or incorrectly adjusted machine parts.
- In winding, warping, and weaving, high tension can cause yarn to break.
Remedies:
- Maintain the machinery to keep it working properly.
- Replace any worn or damaged parts that could cause yarn breakage.
- Ensure that tension is maintained at optimal levels for the yarn being used by regularly monitoring and adjusting it.
- Make sure that defective yarns are identified and removed from production by implementing quality control measures.
- Inspect, test, and sample yarns regularly to make sure only the highest quality yarns are being used.
2. Uneven winding:
An uneven winding occurs when the yarn is not distributed evenly on the package, resulting in low or high density areas. It can be caused by inconsistent tension, improper package formation, or irregular yarn feeding. In order to prevent this from happening, operators should ensure the tensioning devices are operating at a uniform tension. Moreover, they should ensure proper alignment of the winding heads and check the yarn path for obstructions or misguided paths that could cause uneven winding.

Causes of defect:
- Uneven winding can result from insufficient gripping or holding of the yarn during winding.
- Incorrect or irregular traverse movements of the yarn guide can result in uneven yarn distribution.
- The tension settings can be inconsistent or incorrect during the winding process, leading to uneven winding.
Remedies:
- During winding, ensure the yarn gets a good grip and is held tight to prevent slipping.
- Ensure that the tensioning devices and grippers are securely holding the yarn.
- To ensure smooth and even distribution of yarn across the package, optimize the traverse movement of the yarn guide.
- Ensure uniform yarn placement by adjusting traverse speed, stroke length, and guide positioning.
3. Yarn slippage:
During winding, yarn slippage occurs when the yarn slips or slides off the package. It may occur as a result of inadequate tension, inadequate package formation, or improper package dimensions. The tension should be increased slightly to prevent slippage without causing yarn breakage. The package dimensions should also be checked and adjusted to ensure a good grip on the yarn.
Causes of defect:
- During processing, excessive mechanical stress or strain can cause the yarn to slip or move.
- Slippage can occur during various stages of processing due to insufficient gripping or holding of the yarn.
- During winding, warping, or weaving, yarn slippage can occur due to insufficient tension applied.
Remedies:
- Ensure proper functioning of the machinery by regularly inspecting, cleaning, and maintaining it.
- Inspect worn or damaged parts that may contribute to yarn slippage and replace them if necessary.
- Adjust tensioning devices, grippers, or clamps to hold yarn securely during processing.
- Make sure the gripping surfaces are in good condition and provide adequate friction.
4. Yarn tangling or knotting:
When yarn is not properly guided or tensioned during winding, it can tangle or knot. Misaligned guides, improper yarn paths, or excessive tension fluctuations can cause it. Operators should ensure that guides and separators are positioned and aligned correctly along the yarn path to correct this defect. To minimize the risk of tangling or knotting, tensioning devices must also be monitored to maintain a steady and consistent tension.
Causes of defects:
- An excessive or inadequate twist can result in tangling yarns.
- A yarn guide that is poorly positioned or designed can cause the yarn to deviate from its intended path and tangle.
- Yarn tangling can be caused by inadequate or excessive tension applied during winding, warping, or weaving.
Remedies:
- In order to minimize tangling, use yarns with appropriate twist levels.
- To ensure smooth and proper yarn flow, adjust the yarn guides’ positioning and design.
- To prevent snagging and tangling, make sure the yarn guides are free of rough edges or surfaces.
- Make sure the tension settings on the yarn processing machines are correct.
5. Stitch:
During the winding process of yarn onto a bobbin or cone, a stitch defect of yarn winding occurs. The quality and appearance of the final fabric can be negatively affected by this defect. Stitch formation is caused primarily by excessive spindle speed, worn-out spindles and bores of cones and chess, large tension variations during winding, defective yarn release after knotting, incorrect alignment of tension bracket, damaged or worn out drum groves, and incorrect traverse restrictor setting.

Causes of defect:
- Improper setting of traverse restrictors.
- worn out or damage groves in the drum.
- large tension variation during winding.
- Excessive spindle speed.
Remedies:
- Make sure that yarn guides are properly adjusted and aligned.
- It is important to ensure that the yarn is moved through the guides in a smooth manner.
- As needed, replace worn-out or damaged guides with new ones.
- There is a need to maintain damaged groves in the drum.
6. Chafed yarn:
During the winding process, chafed yarn defects are caused by abrasion or wear on the yarn. Fibers can be weakened as a result, which may affect the final fabric quality. During the yarn winding process, chafed yarn defects can be caused by a number of factors. In order to diagnose chafed yarn defects, here are some common causes:
Causes of defect:
- Surfaces that are rough or abrasive, such as yarn guides, tension discs, or bobbins, on winding machine components.
- Yarn guides that are misaligned or damaged, causing friction and rubbing.
- Abrasion can be caused by poorly maintained or worn-out machine parts.
- Abrasion occurs due to inconsistent tension control throughout the winding process.
- Insufficient tension causes the yarn to move or slide within the winding mechanism, causing rubbing and friction.
Remedies:
- Maintain winding machines regularly to ensure smooth operation.
- Ensure there are no rough or abrasive surfaces inside the machine.
- To minimize friction and yarn abrasion, lubricate moving parts.
- To prevent yarn chafing, adjust the tension settings on the winding machine.
7. Soft package:
During yarn winding, a soft package occurs when the wound yarn package is loosely wound and lacks density and stability. During storage, transportation, and subsequent processing, this can cause several problems. Yarn winding soft packages can be caused by the following factors:

Causes of defect:
- The winding process can be affected by inadequate tension, which can result in a soft package. When the tension is too low, the yarn may not be tightly wound onto the package, resulting in a loose and less compact package.
- An unevenly wound package with loose winding can be caused by fluctuations in tension during winding.
- Tension control mechanisms that are inaccurate or tension settings that are not adjusted properly can contribute to inconsistent tension.
- The winding machine may malfunction or have mechanical issues that can result in soft packages.
- There are several components that can affect the winding process and compromise the structure of packages, including tensioning devices, yarn guides, and other components.
Remedies:
- Set the tension on the winding machine appropriately, balancing between too tight and too loose.
- Maintain consistent and appropriate tension levels during the winding process.
- To achieve more accurate and uniform tension throughout the winding process, consider using automatic tension control systems.
- The yarn layering on the package should be observed. Minimize gaps between yarn layers by ensuring even distribution.
- By adjusting the winding parameters, you can achieve a more compact and stable package structure.
8. Collapsed cone:
Collapsed cones occur when a yarn package on a cone collapses or deforms, resulting in a conical shape that is not structurally stable. The result can be difficulties in handling, transportation, and subsequent processing. The following are some common causes of a collapsed cone in yarn winding:

Causes of defect:
- If insufficient tension is applied during winding, the package structure can become loose or weak, leading to a collapsed cone.
- Variations in tension during the winding process can result in an unstable package and collapsed cone.
- If yarn is layered incorrectly or unevenly, the package could collapse.
- If the yarn is wound too loosely or unevenly, it can contribute to the cone collapsing.
Remedies:
- Make sure the tension settings on the winding machine are correct, avoiding both excessive and insufficient tension.
- It is important to layer yarn evenly and densely on a cone, ensuring an even distribution.
- Improve winding parameters, such as traverse speed and yarn guide positioning, for a stable package.
- During winding, adjust the package build parameters to achieve proper tension and support for the yarn.
9. Bell-shaped cone:
In yarn winding, a bell-shaped cone occurs when the yarn package bulges outwards in the middle, resembling a bell. This can cause difficulties when handling, transporting, and processing the material. The following are some common causes of a bell-shaped cone in yarn winding and remedies for it:

Causes of defect:
- During winding, if the yarn is not properly gripped or held in place, it may slip and accumulate excess yarn in the middle, causing the cone to bulge.
- Insufficient traverse movement of the yarn guide across the package can result in uneven yarn distribution and bell-shaped cones.
- Bulging cones can occur when the yarn is not sufficiently tensioned during winding, particularly in the middle section.
Remedies:
- Prevent slippage by gripping and holding the yarn properly during winding.
- To ensure smooth and even distribution of yarn across the package, optimize the traverse movement of the yarn guide.
- Ensure uniform yarn placement by adjusting traverse speed, stroke length, and guide positioning.
- Make sure tension is monitored and adjusted regularly to ensure optimal control, avoiding both excess and insufficient tension.
10. The faulty shape of the package:
In yarn winding, the term faulty shape refers to situations when the package does not have the desired shape, such as when it is uneven, distorted, or irregular. It can be difficult to handle, transport, and process these materials as a result. The following are some common causes and remedies for faulty package shape defects:

Causes of defect:
- During the winding process, inconsistent tension can cause uneven yarn distribution and lead to faulty package shapes.
- A faulty package shape can be caused by improper or irregular traverse movement of the yarn guide.
- Uneven or inconsistent winding angles can result in faulty package shapes due to incorrect yarn layering.
Remedies:
- Ensure that yarn is layered properly on the package, with consistent winding angles.
- To ensure smooth and even distribution of yarn across the package, optimize the traverse movement of the yarn guide.
- Maintain desired package shape by adjusting traverse speed, stroke length, and guide positioning.
- Maintain consistent tension throughout the winding process by ensuring proper tension settings on the winding machine.
11. Formation of ribbon:
In yarn winding, a ribbon is formed when the yarn is wound in a flat or ribbon-like shape, rather than round or cylindrical. There are a number of reasons why this occurs and it can affect the processing and utilization of the yarn in the future. The following are some common causes and potential remedies for ribbon formation:

Causes of defect:
- Ribbons are formed when yarn is wound with insufficient tension, creating loose or slack winding.
- It is possible for yarn layers to be distributed unevenly or irregularly when the yarn guide traverses unevenly or irregularly, leading to the formation of ribbons.
- When the yarn is not gripped or held tightly enough during winding, it can slip and form ribbon-shaped packages.
Remedies:
- Ensure that yarn is distributed evenly across the package by optimizing yarn guide traverse movement.
- Achieve uniform yarn placement and prevent ribbon formation by adjusting traverse speed, stroke length, and guide positioning.
- The winding machine must be set to the proper tension, balancing adequate tightness and not over tensioning.
- Maintain consistent and appropriate tension levels during the winding process.
12. Tight bobbin:
In yarn winding, a tight bobbin occurs when the yarn is wound too tightly on the bobbin, resulting in excessive tension and compression. A number of issues can arise as a result, including difficulties unwinding the yarn, increased breakage, and possible yarn damage. Some common causes and remedies for tight bobbin formation are listed below:

Causes of defect:
- A tight bobbin can form when too much tension is applied during winding.
- The tension control may be improperly adjusted, tensioning devices may malfunction, or tension settings may be incorrect.
- An uneven distribution of yarn or insufficient layering on the bobbin can result in a tight bobbin
- Incorrect traverse movement of the yarn guide can result in concentrated yarn winding in certain areas, resulting in a tight bobbin.
Remedies:
- Ensure even and uniform winding by layering and distributing yarn on the bobbin.
- Ensure that winding parameters such as traverse speed and stroke length are optimized so that the package is well-built and evenly tensioned.
- Avoid excessive tension on the winding machine by ensuring proper tension settings.
13. Imperfect winding speed:
During yarn winding, imperfect winding speed refers to variations or inconsistencies in the rotational speed of the winding process. As a result, the wound package may have uneven yarn tension, uneven yarn placement, or uneven package density. The following are some common causes and potential remedies for imperfect winding speed:
Causes of defect:
- Variations in the machine speed can lead to variations in winding speed, resulting in imperfect winding.
- Inconsistencies in speed can be caused by worn-out parts, misalignment, or improper calibration of the winding machine.
- Operator error can result in imperfect winding speed when the winding machine is not controlled or adjusted correctly.
Remedies:
- Keep the winding machine in optimal working condition by regularly inspecting and maintaining it. Any worn-out or damaged parts may affect speed consistency.
- Maintain a consistent winding speed by calibrating and adjusting the winding machine. Make sure the machine is set correctly according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Maintain a consistent winding speed by implementing or improving speed control systems, such as electronic or computerized systems.
14. Wild yarn:
The term wild yarn refers to yarn that is excessively loose, uncontrolled, or tangled. A number of issues can arise during the fabric manufacturing process, including difficulty handling, increased yarn breakage, and a negative impact on the fabric’s quality. Listed below are some of the most common causes of wild yarn, along with some potential remedies:
Causes of defect:
- Wild yarn can be caused by inadequate tension during winding, warping, or weaving.
- Uncontrolled yarn movement and wild yarn formation can be caused by improper yarn guides or malfunctioning yarn paths.
- Insufficient gripping or holding of the yarn during processing can result in the yarn slipping and becoming wild.
- Insufficient twist, excessive smoothness, and low cohesion make yarns more prone to wild behavior.
Remedies:
- Make sure the tension settings on the yarn processing machines are correct.
- Ensure that the yarn guides are positioned and designed correctly to ensure a controlled movement of the yarn.
- Make sure the tensioning device, gripper, or clamps are working properly so that the yarn stays in place during processing.
- In order to minimize wild yarn formation, choose yarns with the appropriate twist level for the intended application.
15. Mixing of Different Linear Densities Yarn:
During the winding process, different linear densities of yarn are unintentionally mixed together. This can result in inconsistencies in the fabric’s appearance, texture, and performance. These are some of the most common causes of mixing different linear densities of yarn and what can be done about them:
causes of defect:
- Various linear densities can be mixed when yarn packages are misidentified or incorrectly labeled.
- The mixing of yarns of different linear densities can be caused by inadequate separation during storage or handling.
- The winding machine settings can be incorrect or inadequate and can result in different yarn linear densities mixed together.
- This defect can be caused by improper calibration or adjustments of machine parameters, such as tension, traverse speed, or package size.
Remedies:
- Set up and calibrate the winding machine properly to avoid mixing different linear densities. Check the machine parameters, such as tension, traverse speed, and package size, according to the yarn specifications.
- Assure that yarn of different linear densities is segregated and organized properly in the storage area.
- Make sure yarn packages are properly identified and labeled through quality control measures.
- Verify the linear density specifications before winding yarns.
16. Nose bulging:
Yarn nose bulging is a common defect in the winding process that can affect wound yarn packages in terms of appearance and functionality. An uneven and irregular shape is caused by the yarn layers protruding from the sides of the package. Factors such as improper tension control, inadequate yarn guide positioning, and excessive yarn buildup at package edges can cause nose bulging.

Causes of Defect:
- Bulging of the nose occurs when yarn layers protrude from the sides of the wound package.
- Inconsistent tension settings can result in variations in yarn layer thickness and nose bulging. An insufficient tension can create loose layers that bulge out, while an excessive tension can result in compacted layers that bulge out.
Remedies:
- The tension devices on the winding machine must be set and controlled accurately.
- Ensure yarn guides are properly positioned and aligned to ensure the yarn is guided onto the package smoothly without excessive friction or pressure.
- Ensure yarn guides are regularly inspected and maintained.
Conclusion:
Textile products can be adversely affected by yarn winding defects. Improper tension, inadequate winding techniques, machine malfunctions, or low-quality yarns can cause defects. These defects, however, can be minimized or eliminated with appropriate understanding and implementation of appropriate remedies, ensuring better yarn winding and ultimately increasing textile product quality. However, if you have any question about yarn winding defects , let me know below comment box.