Name of Experiment:
Study on differences between welding and molding in garments manufacturing.
Introduction:
The seamless integration of various techniques and processes is a key component for apparel manufacturers to achieve high-quality and innovative products. In spite of the numerous methods employed, welding and molding have emerged as two prominent techniques with distinct applications and characteristics. In order to select appropriate welding and molding techniques for specific production requirements, garment manufacturers must understand the fundamental differences between the two.
In garment manufacturing, welding is often associated with fabric joining. It involves the fusion of fabric materials using heat or pressure. Fabric pieces can be seamlessly integrated using the welding process, eliminating the need for stitching or sewing, as it creates strong and durable bonds. The benefits of welding include improved aesthetics, enhanced comfort, and longer wear life.
A molding technique is also commonly used in producing three-dimensional clothing and accessories and involves shaping or forming fabric materials with heat, pressure, or both. By using molds or forms to shape the fabric into desired configurations, molding allows for the creation of intricate and structured designs. By using the molding process, manufacturers can achieve unique and complex designs that are difficult to replicate with traditional sewing.
While welding and molding share the common goal of fabric integration, their different characteristics make them suitable for different applications in garment manufacturing. Choosing between welding and molding techniques is influenced by factors such as fabric type, garment design, production scale, and desired outcomes. Therefore, manufacturers, designers, and industry professionals must conduct a comprehensive study to distinguish between welding and molding to optimize production processes and improve the quality and aesthetics of garments.
In this experiment, we will analyze the principles of welding and molding techniques, explore their applications in various garment sectors, examine the advantages and challenges associated with each method, and examine case studies to illustrate how it is applied in real-life situations. This study aims to shed light on how to select the right technique for specific garment manufacturing needs, promoting innovation, efficiency, and excellence.
Objectives:
- Identify the principles and mechanisms underlying the manufacturing of garments by welding and molding.
- The purpose of this study is to identify the specific applications and suitability of welding and molding techniques for different types of garments and accessories.
- Analysis of the advantages and limitations of welding and molding in terms of product quality, durability, aesthetics, and comfort.
- Understanding the basic differences between welding and molding.
- To know working process of welding and molding.
Welding in the Garments Manufacturing:
Welding is one of the most commonly used techniques in garment production in which fabric materials are fused or welded together without the use of traditional stitching or sewing techniques. Welding involves the use of heat, pressure, or a combination of both to create a strong and durable bond between fabric materials. In order to complete the process, the following steps must be followed:
- Fabric Preparation: The fabric pieces to be welded are cut into the desired size and shape. They must be clean, smooth, and free of frayed or loose threads.
- Welding Method Selection: In garment manufacturing, a variety of welding methods can be used depending on the type of fabric, the design of the garment, and the desired outcome. Some common welding methods include heat sealing, ultrasonic welding, radio frequency welding, and hot air welding.
- Heat Sealing: Heat sealing is commonly used to join synthetic fabrics or materials with thermoplastic coatings because it uses heat to melt fabric surfaces, which are then pressed together to form a bond.
- Ultrasonic Welding: A wide range of fabric types may be welded using ultrasonic welding, which involves using high-frequency sound waves to create heat between the fabric layers. It can create precise and strong welds with a wide range of fabric types.
- Radio Frequency (RF) Welding: RF welding produces strong and watertight seams by generating heat within the fabric through electromagnetic waves. RF welding is often used for thicker or multilayered fabrics.
- Hot Air Welding: During hot air welding, heated air is directed onto the fabric surfaces to melt and bond them together. This method is suitable for fabrics that can withstand high temperatures and is commonly used in industrial settings
3. Welding Equipment Setup: Welding equipment is set up according to the welding method chosen, including adjusting temperature, pressure, and other parameters.
4. Welding Process Execution: When the fabric pieces are placed in the welding equipment, the desired areas to be welded are aligned properly. The welding equipment covers the fabric surfaces with heat, pressure, or a combination of both.
5. Cooling and Finishing: After welding, the fabric is cooled and solidified, forming a strong bond. Any excess seams and materials are then trimmed, and the finished fabric piece is inspected.
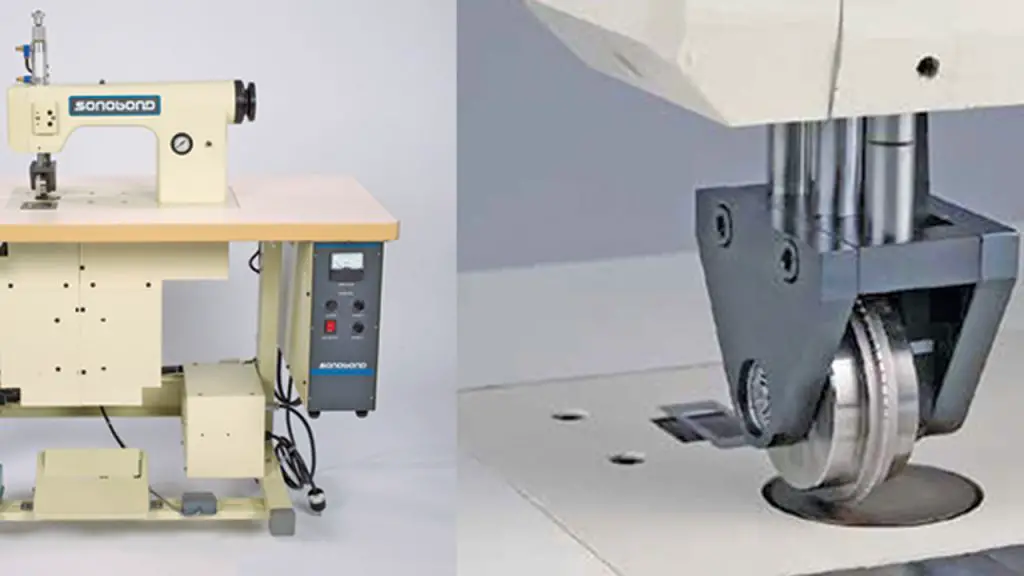
In garment manufacturing, welding offers a variety of advantages, including improved durability, improved aesthetics, enhanced comfort, and shorter production times. It is particularly useful for creating seamless designs, joining synthetic fabrics, and producing waterproof or airtight seams. The efficiency and innovation of garment manufacturing processes is enhanced by welding techniques, which eliminate the need for traditional sewing.
Molding in the Garments Manufacturing:
A mold is a process by which fabric materials are shaped or molded into three-dimensional structures using heat, pressure, or a combination of both in garment manufacturing. Through molding, intricate and structured designs can be created that cannot be achieved through traditional sewing methods. Typically, the molding process involves these steps:
- Fabric Selection: Based on the desired outcome of the garment or accessory, fabrics with suitable molding characteristics, such as flexibility, drapeability, and heat resistance, are selected. Fabric blends containing thermoplastic components, synthetic fibers, and thermoplastic materials are commonly used for molding.
- Mold Preparation: A mold or form is made depending on the shape and structure of the garment or accessory. Molds can be made from plastic, rubber, or metal depending on the specific requirements.
- Fabric Preparation: A fabric piece is prepared for molding by cutting it into the desired shape and size, keeping in mind the allowances for molding and seam allowances. Pre-treatments, such as heat-sensitive adhesives or treatments, are then applied to the fabric to enhance its moldability.
- Fabric Placement: To obtain the desired three-dimensional shape, fabric pieces are carefully placed on the prepared mold or form, adhering to its contours and curves.
- Molding Method Execution: In garment manufacturing, vacuum molding, compression molding, temperature-forming, and injection molding are common molding techniques used to shape fabric onto the mold or form.
- Cooling and Demolding: In order for the final garment or accessory shape to be revealed, the fabric is allowed to cool and solidify while still on the mold. Once cooled, the fabric is carefully removed from the mold or form.
- Finishing and Assembly: In addition to modifying the molded fabric pieces, it may also be necessary to add reinforcements, or attach closures or components. This process completes the garment or accessory, which can then be checked for quality and distributed.
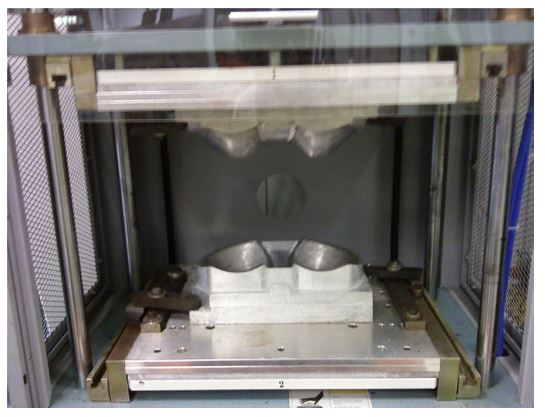
In garment manufacturing, molding techniques allow for the creation of unique and complex designs, offering benefits such as precise shaping, structural integrity, and the ability to incorporate intricate details. Fashion can take advantage of it for innovative garment constructions, voluminous silhouettes, and architectural elements. With their ability to manipulate fabrics in new ways, molding contributes to the evolution and creativity of the garments industry.
Differences Between Welding and Molding:
| S/N | Welding | Molding |
| 01 | The welding process involves bonding or fusing fabric materials without stitching. | In molding, fabric materials are shaped or formed into three-dimensional structures. |
| 02 | The welding technique bonds fabric pieces together, creating a solid bond. | During molding, fabric materials are shaped or molded onto pre-prepared forms. |
| 03 | For seam sealing, hemming, or creating waterproof or airtight seams, welding techniques are commonly used. | Intricate designs, voluminous silhouettes, architectural shapes, and unique textures can be created with molding techniques. |
| 04 | The primary function of welding techniques is to bind fabric pieces together seamlessly, which limits their design flexibility. | Using molding techniques allows designers to create intricate and structured designs that are more flexible. |
| 05 | The stitching is not visible in welded seams, which gives the garment a seamless appearance. | Fabric surfaces may be visible seams or fold lines as a result of molding techniques. |
| 06 | Welded fabric joints are difficult to repair or alter due to the fused bond that is difficult to undo without compromising the integrity of the fabric. | The repair or alteration of molded garments or accessories can be more challenging than that of traditional sewn garments. |
| 07 | Both small-scale and mass-production welding techniques can be used. | Generally, molding processes are better suited to small-scale or specialized production due to the need for special molds or forms. |
Conclusion:
Embracing the differences between welding and molding allows garment manufacturers to better understand these techniques, select the most suitable approach, and drive innovation in the manufacture of high-quality, durable, and aesthetically appealing garments and accessories. A dynamic interplay between welding and molding ensures the garments industry’s adaptability to ever-changing consumer demands and market trends, allowing it to grow and evolve continuously. We learned a lot from this experience and we also learned the difference between welding and molding. Thanks to the teacher for all the help we received.







I value the blog post. Fantastic.
thanks.
Really informative post.Much thanks again. Fantastic.
please share our article…
Awesome blog article.Thanks Again. Really Cool.
please support us….
Thanks again for the blog article.Much thanks again. Will read on…
keep visiting our site.
Really enjoyed this blog article.Much thanks again. Keep writing.
keep visit our site…
There’s definately a great deal to find out about this topic. I like all the points you have made.
Thank you dear. Stay with us. Happy reading.
Very informative blog post.Much thanks again. Will read on…
thnx…
I really enjoy the blog. Cool.
keep visit our site…thank too…
Appreciate you sharing, great article.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
keep visit our site…
Really appreciate you sharing this blog article.Much thanks again. Really Cool.
You completed a number of fine points there. I did a search on the issue and found most persons will consent with your blog.
Keep visit our site
You’ve made your point!college essay edithelp writing thesis
Thanks
Hello my family member! I wish to say that this article is awesome, great written and come with almost all vital infos. I’d like to see more posts like this .
Thanks a lot
Aw, this was a very nice post. In concept I wish to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and precise effort to make a very good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and not at all seem to get one thing done.
Article writing is also a fun, if you know after that you can write orelse it is complex to write.
There is certainly a great deal to know about thissubject. I love all the points you have made.
constantly i used to read smaller articles or reviews that as well clear their motive, and that is also happening with thispost which I am reading at this time.
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic article.Really looking forward to read more. Much obliged.
I value the blog.Much thanks again. Great.
Thanks for the article post.Really thank you! Really Cool.
Hello, every time i used to check blog posts here in the early hours in thedawn, as i enjoy to learn more and more.
keep visiting our site….
I cannot thank you enough for the blog post.Really thank you! Great.
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic post.Much thanks again. Will read on…
I loved your blog article.Really thank you! Much obliged.
Appreciate you sharing, great article post. Want more.
Appreciate you sharing, great article post.Thanks Again. Really Cool.
keep visit our site….
Thanks a lot for the blog article.Much thanks again. Awesome.
Looking forward to reading more. Great blog. Really Great.
Major thankies for the post.Much thanks again. Much obliged.
Truly no matter if someone doesn’t be aware of then its up to other users that they will help, so here it happens.
A fascinating discussion is definitely worth comment. I believe that you need to publish more about this subject matter, it may not be a taboo matter but generally people do not speak about such issues. To the next! Kind regards!!
I think this is a real great blog.Really looking forward to read more. Will read on…
Wow, great blog.Much thanks again. Much obliged.
Really appreciate you sharing this article.Much thanks again. Keep writing.
Really appreciate you sharing this article post.Thanks Again. Will read on…
Wow, great article. Really Cool.
I think this is a real great article post.Really looking forward to read more. Awesome.
Really enjoyed this article post.Really thank you!
A round of applause for your post.Much thanks again. Will read on…
Im thankful for the article post. Fantastic.
Thanks for sharing, this is a fantastic blog post.Much thanks again. Really Cool.
Thanks for the article.Thanks Again. Cool.
Fantastic post.Much thanks again.
Thanks so much for the article.Much thanks again. Want more.
Thanks so much for the blog.Much thanks again. Much obliged.
Very informative post.Much thanks again.
I truly appreciate this blog.Really looking forward to read more. Will read on…
I really like and appreciate your blog post.Really looking forward to read more.
Say, you got a nice blog post.Really looking forward to read more. Want more.
Thanks so much for the blog article.Thanks Again. Really Great.
Thanks so much for the article.Really looking forward to read more.
I value the post.Much thanks again. Great.
I really enjoy the article.Thanks Again. Cool.
Im grateful for the blog post.Thanks Again.
I truly appreciate this article.Really thank you! Awesome.
I really enjoy the post. Fantastic.
Im thankful for the blog. Really Great.
Very good article post.Much thanks again. Will read on…
Thanks a lot for the post.Really thank you! Really Great.
I think this is a real great blog post.Much thanks again.
Really informative blog.Really looking forward to read more. Awesome.
I really like and appreciate your blog article.Thanks Again. Really Great.
Fantastic article. Great.
I really enjoy the blog. Really Cool.
Looking forward to reading more. Great post.Really thank you! Really Great.
Great, thanks for sharing this article post.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
Im thankful for the article. Want more.
Wow, great blog post. Really Cool.
You are a very smart person!
Im grateful for the article post.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
Awesome blog article. Really Great.
Thanks for the blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great.
Really enjoyed this article.Really thank you! Much obliged.
Wow, great blog post. Awesome.
I really like and appreciate your blog.Really looking forward to read more. Awesome.
Im obliged for the article post.Thanks Again. Keep writing.
Say, you got a really great blog post.Many thanks again. Really Great.
Thanks for the blog.Really looking forward to read more. Keep writing.
Great, thanks for sharing this article post.Really thank you! Great.
I appreciate you sharing this blog post.Much thanks again. Want more.
Really appreciate you sharing this post.Really looking forward to read more. Much obliged.
Say, you got a nice article post.Really thank you! Want more.
Thank you for your post.Really thank you! Keep writing.
Enjoyed every bit of your blog article.Really thank you! Keep writing.
I think this is a real great blog. Will read on…
I like reading through a post that can make people think. Also, thanks for allowing me to comment.
Really appreciate you sharing this post.Really looking forward to read more. Great.
Hey, thanks for the blog.Thanks Again. Fantastic.
I loved your article post.Much thanks again. Awesome.
Very neat post.Much thanks again.
I appreciate you sharing this article.Really thank you! Really Great.
A big thank you for your article post.Really thank you! Really Great.
A big thank you for your article.Much thanks again.
Really informative blog article.Much thanks again. Cool.
Major thanks for the blog.Really thank you! Really Cool.
Thanks for the blog article.Really thank you! Fantastic.
Thanks a lot for the article post.Thanks Again. Want more.
A fascinating discussion is worth comment. There’s no doubt that that you ought to publish more on this issue, it may not be a taboo subject but generally folks don’t talk about these topics. To the next! Many thanks!!
I like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for permitting me to comment!
Thanks
I truly appreciate this post.Much thanks again. Really Great.
Great article. I will be facing a few of these issues as well..
I value the blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Want more.
Appreciate you sharing, great blog. Want more.
Thank you for your blog post.Really thank you! Really Great.
Appreciate you sharing, great article post.Thanks Again. Really Great.
Very informative blog article.Thanks Again. Will read on…
Thanks again for the blog article.Thanks Again. Keep writing.
I am so grateful for your post. Really Great.
Hi! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Carry on the great work!
I am so grateful for your blog article.Really looking forward to read more. Awesome.
This article gives clear idea for the new people of blogging,that actually how to do running a blog.
Thanks
I really like and appreciate your post.Really looking forward to read more.
A big thank you for your blog.
A big thank you for your blog article.Thanks Again. Really Great.
Im obliged for the blog.Really thank you! Want more.
Hey! I enjoyed this blog post. Thanks for writing it. I’ll be back to read more.
Very good blog post. Awesome.
I truly appreciate this article post.Really looking forward to read more. Really Cool.
I am so grateful for your article.Really thank you! Awesome.
Really informative article.Really thank you! Will read on…
I value the article post.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Enjoyed every bit of your article post.Really looking forward to read more. Cool.
Enjoyed every bit of your blog post.Really thank you!
Thanks a lot for the blog post.Much thanks again. Really Great.
I truly appreciate this article post. Want more.
Thank you ever so for you blog.Much thanks again. Cool.
Hey, thanks for the blog.Thanks Again. Keep writing.
The narrative was strong, but adding images would make it stronger!
Really enjoyed this article.Really looking forward to read more. Keep writing.
This is one awesome blog article.Really thank you! Really Great.
Great blog post.
Great blog post. Really Great.