Introduction:
An initial stage in the spinning process is the blow room. As a result of the airflow, the name blow room was given. Due to airflow, all processes take place in the blow room. Different machines in the blow room perform the objectives of the blow room. Cotton tufts become smaller and smaller in the blow room. Trutzschler blow room line is a popular in the cotton spinning sector.
Trützschler Group is a German manufacturer of textile machinery based in Mönchengladbach. A family business is divided into three business units: Spinning, Nonwovens & Man-Made Fibers, and Card Clothing. A total of eight factories worldwide produce machines, installations, and accessories for spinning preparation, nonwovens, and man-made fibers. In addition to its four factories in Germany, Trützschler has production sites in China (Shanghai), India (Ahmedabad), the United States (Charlotte), Brazil (Curitiba), and Switzerland (Winterthur). The important textile processing areas of Bangladesh, Vietnam, Indonesia, and Pakistan are served by service centers.
Objectives:
- To know about blow room.
- To know flow chart of blow (Rieter)
- Function of different machine of blow room.
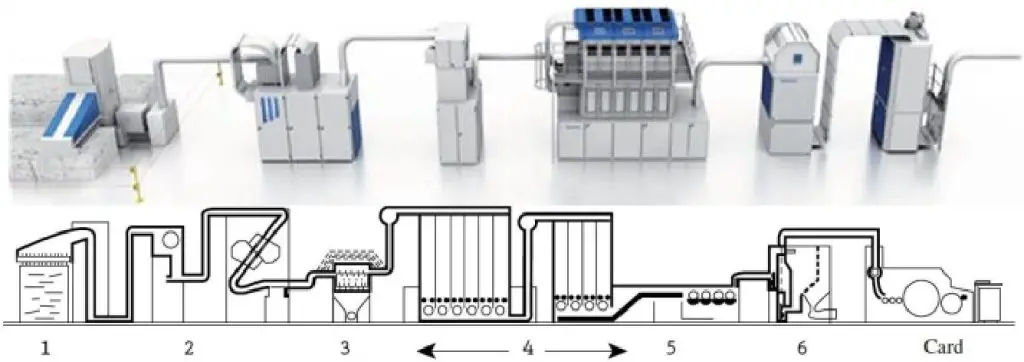
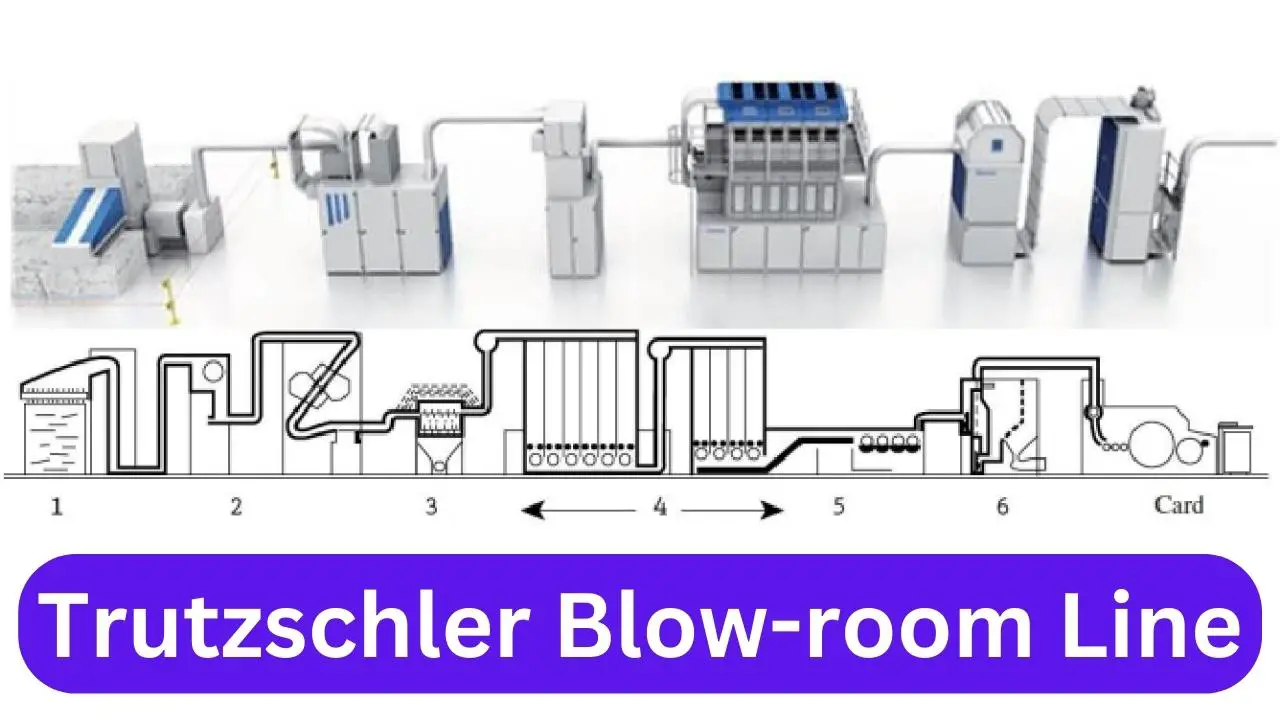
Flow Chart of Trutzschler Blow Room Line:
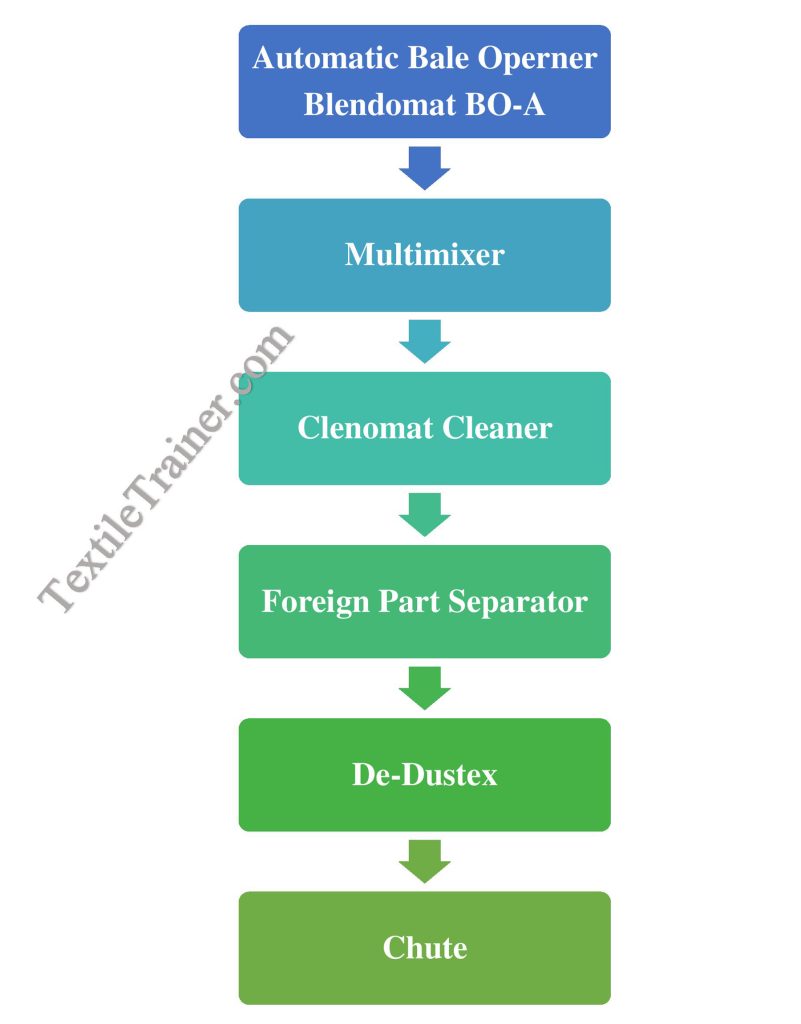
A brief description of the flow chart is given below.
1. Automatic Bale Opener BO-A:
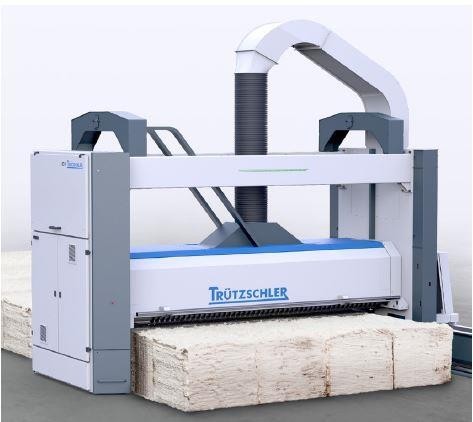

The BO-A can be adapted to a variety of spatial conditions, providing one-row and two-row bale laydowns, as well as feeding three cleaner lines and an opener line. In order to achieve quality, tuft flow from its gentle bale opening must be homogeneous.
It has some special characteristics. They are:
- Capacity of 2,000 kilograms per hour.
- Working off of 1 to 3 bale groups per work area, optionally on one or both sides.
- Up to 200 bales can be laid down for extended, unattended operations.
- There is the possibility of different bale heights.
- Work-off area for a complete reserve set of bales: Working width maximum. Up to 50 m in length and 2,300 mm in diameter.
- Continual performance in both directions.
2. Multi-mixer
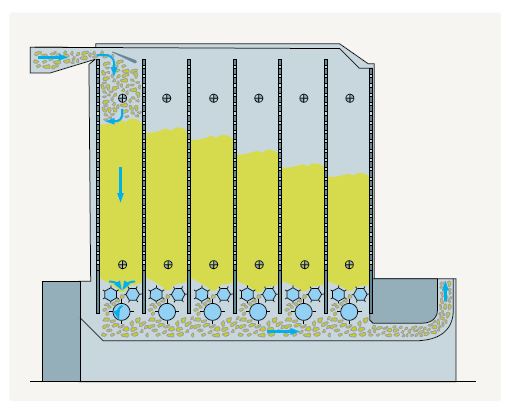
As a leading manufacturer of one-component staple fiber blends, Trützschler mixer systems offer a wide range of solutions for all applications:
- Mixers of different sizes for different needs
- High homogeneity due to controlled, reproducible blending.
- Optimized blend for uniform product appearance.
During a temporary absence of material, the mixer automatically switches to Energy mode. The fan speed is reduced to an energy-saving minimum when Saving Mode is activated.
3. Clenomat Cleaner:
Clenomat cleaners are also available in stainless steel finishes. All material-carrying parts are made of stainless steel. A reviving agent is prevented from accumulating on this equipment, resulting in considerably safer fiber transport. Clenomat cleaners in stainless steel finish are ideal for customers who want to process various types of fibers:
- Cotton
- Man-made fibers
- Cotton and man-made fiber blends
- Secondary fibers made from textile waste
It has some special characteristics. They are:
- Self-optimization of cleaning quality.
- Effectively removes fine dust.
- Technology that is excellent for cleaning using WASTECONTROL.
- Feeding of cards continuously without stopping and starting.
- An easy-to-use color touch screen.
- Using four rolls of feed, we can achieve production rates up to 1,200 kg/h.
- A large cleaning roll and two cleaning elements make up the core of the cleaner.
4. Foreign Part Separator:
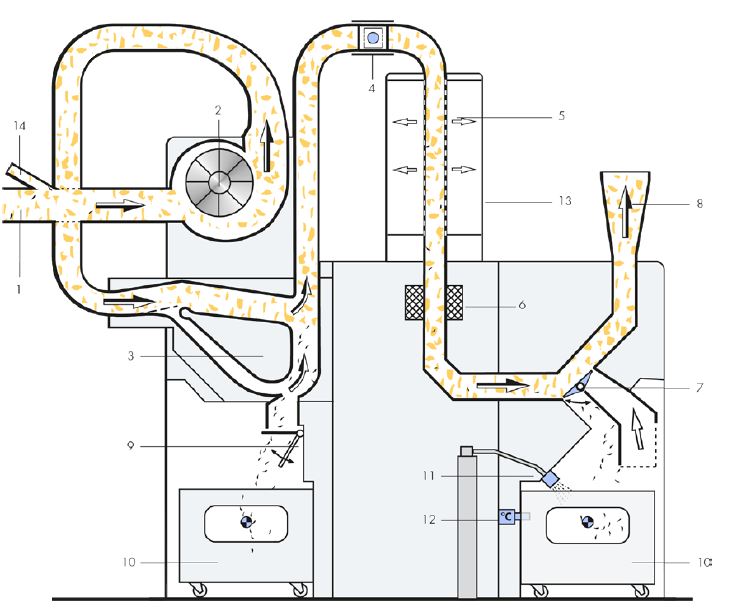
1=The material is suctioned by a Portal Bale Opener BO-A.
2 =The automatic control of the fan ensures uniform air volume.
3= A new guiding profile has been developed for the aerodynamic heavy part separator.
4= The rectangular duct is monitored by two spark detectors.
5= The dusty air is extracted in the air separator.
6= The metal detector detects all types of metals
7= The extraction flap does not work with pre-tensioned springs, but is actively opened and closed.
8= The next machine (e.g. fan in front of mixer) suctions off material
9= A flap conveys the separated heavy parts into the waste cart
10= Both waste carts are generously dimensioned.
11= An extinguishing nozzle is installed at this point.
12 =A heat detector monitors the waste container.
13= The dusty exhaust air is fed to a filter system.
14 =Opened waste from the Waste Opener BO-R can be fed back without an additional fan.
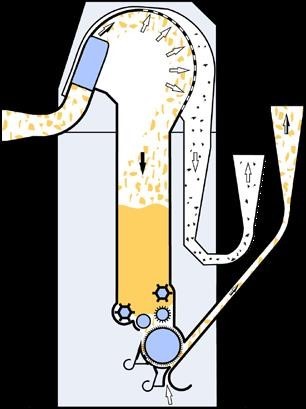
5. De-Dustex:
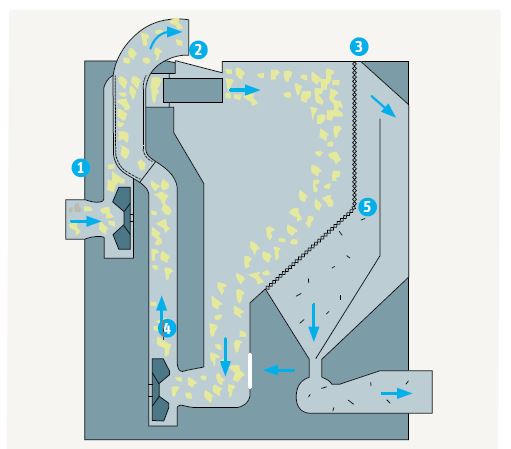
1= This fan sucks the materials off the cleanomate cleaner.
2= The distribution flaps distribute the tufts over the working width of 1.6 m.
3= Considerable de dusting is effected by the tufts hitting the perforated surface.
4= The material drops into the suction system and is transported to the cards by the variable speed fan.
5= The separated dust is permanently discharged
A large chamber (3) and a perforated sheet (2) are the main components of this machine, as are the infeed (1/2) and withdrawal (4) of the material. In the chamber itself, material tufts are blown against a perforated sheet (3). When the dust is extracted, they slide down the sheet into the funnel (4) and pass to the suction.
Conclusion:
Blow room is the first working zone in short staple spinning. The first and preliminary predominance mechanical load is applied to fiber enormously in this zone. Therefore, blow room is important section in short staple spinning in term of technology. From this experiment we came to learn blow room line of Trutzschler. This experiment will help in our practical field. Thanks to our teacher to help us.
References
- Chowdhury, M. F. (2016). Manual of Short Staple Spinning . Dhaka: Granthanir Prokashoni.
- Trutzschler manual for blow room.
- Klein, W. (2019). The Rieter Manual of Spinning. Switzerland: Rieter Machine Works Ltd.





9 thoughts on “Study on Flow Chart of Trutzschler Blow Room for Cotton Spinning”