Introduction:
The cotton blow room has a special Multi Function Separator (SP-MF) device positioned downstream of the Portal Bale Opener (BO-P). What makes this separator so impressive is its ability to handle high production rates of up to 2,000 kg/h while ensuring reliable performance. One of the standout features of the Multi-Function Separator is its integrated microcomputer control system. This advanced technology ensures all its functions work seamlessly, even at high production rates. It’s designed to be dependable, providing a consistent and efficient operation throughout the cotton processing workflow. Combined with the Portal Bale Opener (BO-P) and the Automatic Bale Opener (BO-A), the Multi Function Separator takes energy-saving to a new level. It cleverly adjusts its fan speed based on the cotton bales’ position, optimizing its performance while reducing energy consumption. multifunctional separator works as protective device.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the Multi Function Separator (SP-MF) working principle and explore how its integrated control system and energy-saving capabilities contribute to a more efficient and sustainable cotton processing process. Let’s unravel the simplicity behind this remarkable device and understand its impact in the cotton blow room.
Function of Multi Function Separator in Blow Room:
The Truetzschler Multi function Separator: SP-MF is used in the Cotton Blow Room to perform the following functions:
- Metal Separation: The SP-MF is equipped with an electronic sensor that detects metal parts around the fiber channel. As a result of its active movement, the subsequent extraction flap responds quickly in both directions. This replaces the traditional wear-intensive spring pretensioning process.
- Fire Protection: Sensors are installed on the machine to reduce fire damage. They are connected to the installation control.
- Waste re-feeding: Waste such as opened cards and draw frame slivers can easily be re-fed without the usual fan: They are sucked up together with the main material flow and are also checked for metal particles.
- Damage prevention: SP-MF separates metal parts from cotton tufts, preventing direct contact between metal parts and beaters. As a result, it protects beaters from damage.
- Quality yarn production: It ensures that the cotton fibers are clean and pure by effectively eliminating impurities such as metallic parts, dust, and other contaminants. The SP-MF contributes significantly to the production of high-quality yarn. With this cleaner fiber stream, yarns are produced with fewer defects, are stronger, and have better quality.
Working Principle of Multi Function Separator: SP-MF
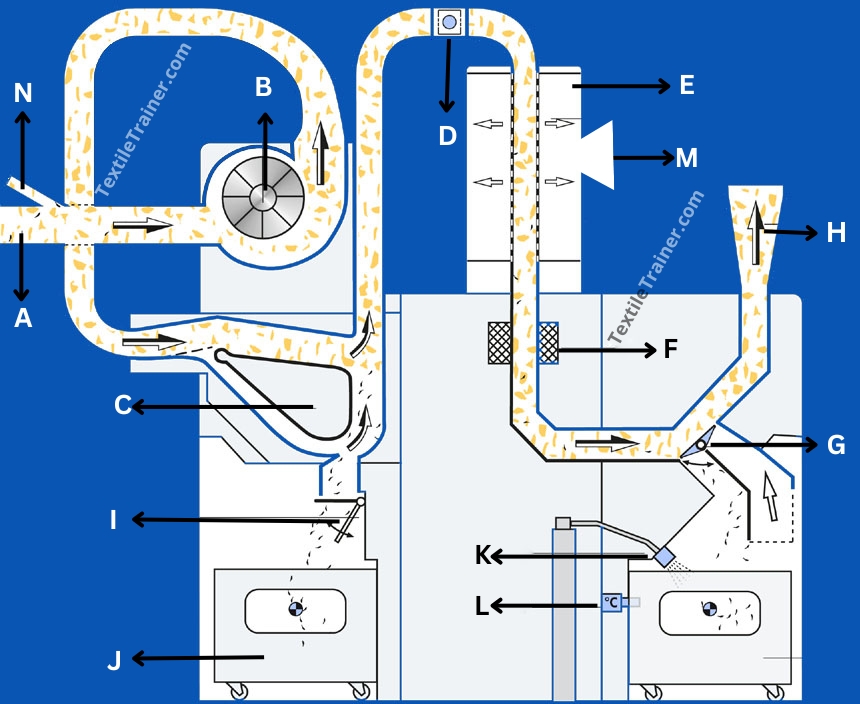
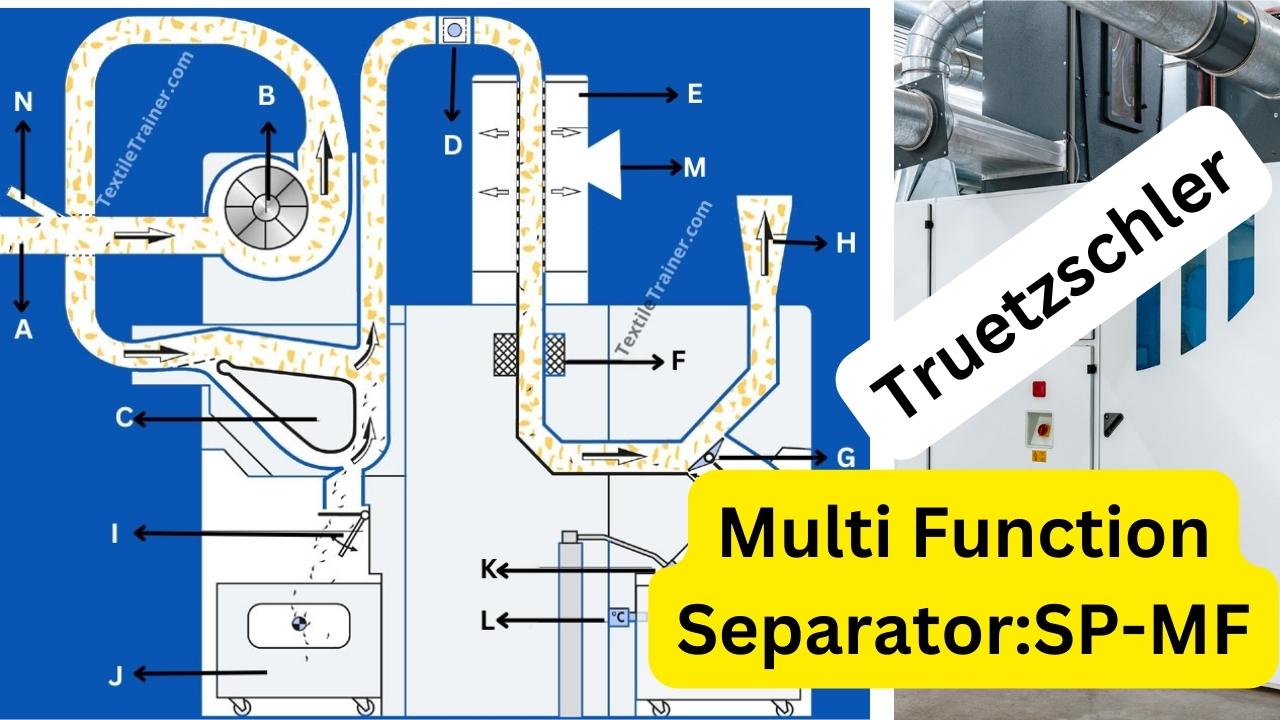
| A= The material is suctioned by a portal bale opener (BO-P) | H= The next machine (e.g. fan in front of mixer) suctions off material. |
| B= The automatic control of the fan ensures uniform air volume. | I= A flap conveys the separated heavy parts into the waste cart. |
| C= A new guiding profile has been developed for the aerodynamic heavy part separator. | J= Both waste cars are generously dimensioned. |
| D= The rectangular duct is monitored by two spark detectors. | K= An extinguishing nozzle is installed at this point. |
| E= The dusty air is extracted in the air separator. | L= A heat detector monitors the waste container. |
| F= The metal detector detects all types of metals. | M= The dusty exhaust air is fed to a filter system. |
| G= The extraction flap does not work with pre-tensioned springs, but is actively opened and closed. | N= Opened waste from the waste opener BO-R can be fed back without an additional fan. |
Tufts (A) from the automatic bale opener and tufts (N) from the waste opener are sucked into the multi functional separator (F) by a fan (B). The arrows indicate the flow path of the tufts. The small black dashes represent the heavy trash particles and the black dots metallic fragments embedded in some tufts. These fragments may result from damaged machine parts during the harvesting and ginning of cotton. The first action of air currents occurs at (C) where the flow path splits into two; the material being prevented from moving along the lower path. Since the airflow rate is constant through this section of the machine, the splitting of the path means a slower flow in the upper path. The bends of 900 angle give a sudden change of direction to the airflow. The lift due to the combined airflow from both flow paths is sufficiently larger than the momentum and gravitational force on each tuft to move tufts in the changed direction. However, the air-drag is not greater than the opposing momentum and gravitational force on the more dense foreign particles. Consequently these drop from the airflow and are collected via a trop door (I) into a waste bin (J), whilst the liberated dust and trash particles remain in the airflow. The second action of air currents occurs at (E). Here a perforated metal sheet or wire mesh enables the dust particles in the flow to be removed through (M); the dusty exhausted air is fed to a filter installation. Small pieces of metallic materials may remain trapped within some tufts, in which case these are detected by sensors at (F), and a diverter (G) momentarily changes the direction of flow so that these tufts can be ejected to waste. The remaining fiber tufts subsequently exit through (H) to the opening/ pre-cleaning unit. With combustible materials, there is always the possibility of tufts being ignited from sparks caused by metal particles impacting on the sides of the air trunking. Buring or smouldering tufts will nned to be removed before reaching the opening/ pre-cleaning stage. A detector (D) signals the diverter (G) to redirect any ignited material to the waste bin (J). A fire extinguisher (K) and heat sensor (L) are fitted safety provisions for any burning material entering the waste container.
Conclusion:
Truetzschler multi functional separator works in protective cleaning zone. This machine used for separate metal parts from cotton tufts. If these material flows with tufts to the beating points then damage of beater wire and fire-n occurrence takes place. So this machine play important role in cotton blow room.
References:
- Chowdhury, M. F. (2016). Manual of Short Staple Spinning. Dhaka: Granthanir Prokashoni.
- Corbman, D. P. (1983). Textiles Fiber to Fabric. NewYork: Mary McGarry.
- Hossain, M. S. (2014). Introduction to Textile Engineering. Dhka: Books Fair Publications.
- Kadolph, S. J. (2006). Textiles. New Delhi: Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd.
- Truetzschler manual for spinning