Name of the Experiment:
Study on scouring of cotton fabric with standard recipe.
Introduction:
Typically, cellulosic fibers are boiled off in an alkaline solution in order to remove natural impurities. Natural impurities such as mineral matters, oils, waxes, and ashes interfere with dye penetration into fibers, leading to waste of dyes and chemicals as well as uneven dyeing due to improper scouring. These factors lead to a large amount of dye and chemical wastage. Alkali treatment with auxiliaries at high temperatures removes the inherent and added impurities from cotton and other cellulosic fibers. The process parameters and concentration of alkalis need to be adjusted depending on the amount and structure of impurities present in the cotton and other cellulosic fiber. In this experiment, we will perform a scouring experiment on cotton fabric in order to remove these impurities, such as oil and waxes. As a result of the removal of these impurities, the fabric becomes more absorbent.
Objectives:
- To know about scouring.
- Come to learn typical recipe for scouring of cotton fabric.
- To know procedure of scouring process of cotton fabric.
- Come to learn functions of scouring chemicals.
Mechanism of Scouring:
The following are the main points related to the mechanism of scouring:
- Saponification: The vegetable oil, which is immiscible with water, is glyceride of fatty acids. When such oil is heated with sodium hydroxide (Caustic soda) in water, the oil splits apart into its constituents fatty acids and glycerine. Sodium hydroxide, which is present in the solution, reacts with glycerine to form sodium salt, which is also soluble in water, removing the oil from the solution.
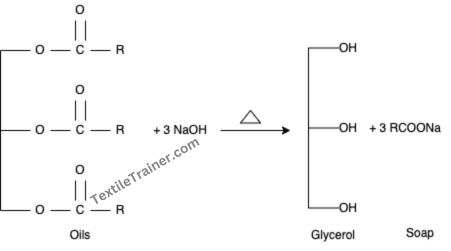
2. Emulsification: By emulsifying, waxes and non-saponifiable oils (non polar) are removed, as they are immiscible with water (polar). Normal soap is used as an emulsifying agent to make emulsions. Saponified soap is also used as an emulsifying agent.
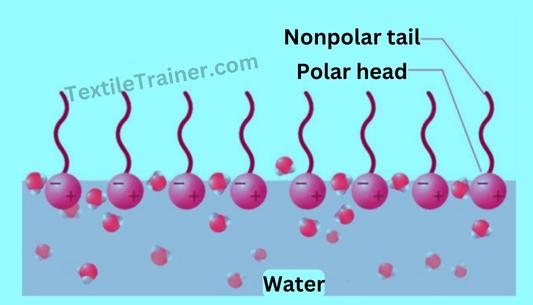
3. Detergency: During handling, dust and dirt are deposited on textile materials; these impurities are also distributed in the scouring liquid and are likely to be returned to the material after scouring. As a wetting agent, all detergents are effective as they keep solid particles suspended in the scouring liquor and prevent them from settling on the cloth and causing deposition.
Typical Recipe for Scouring of Cotton:
| Chemical | Amount (gm/l) |
| Wetting agent | 0.5-1.0 gm/l (Stock solution 1%) |
| Detergent | 1.0-2.0 gm/l (Stock solution 1%) |
| Sequestering agent | 1.0-3.0 gm/l (Stock solution 1%) |
| Caustic soda | 2.0-4.0 gm/l (Stock solution 1%) |
| Temperature | 95-1000C |
| Time | 15-45 min |
| pH | 10.5-11.0 |
| M:L | 1:20 |
| Sample Weight | 5 gm |
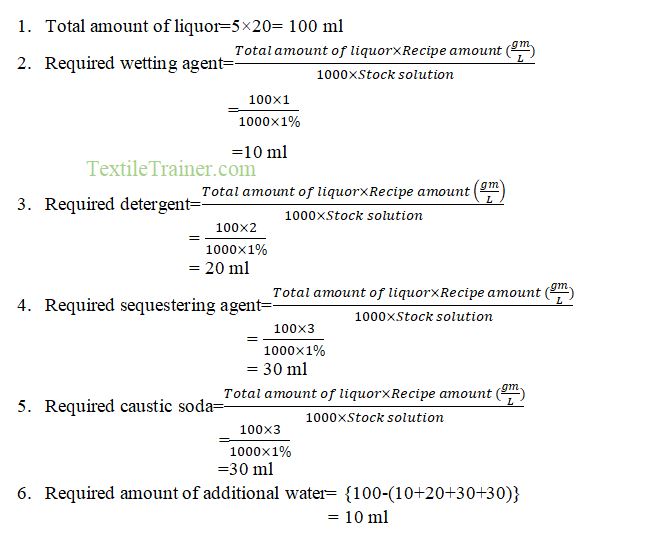
Recipe Calculation:
Process Curve:
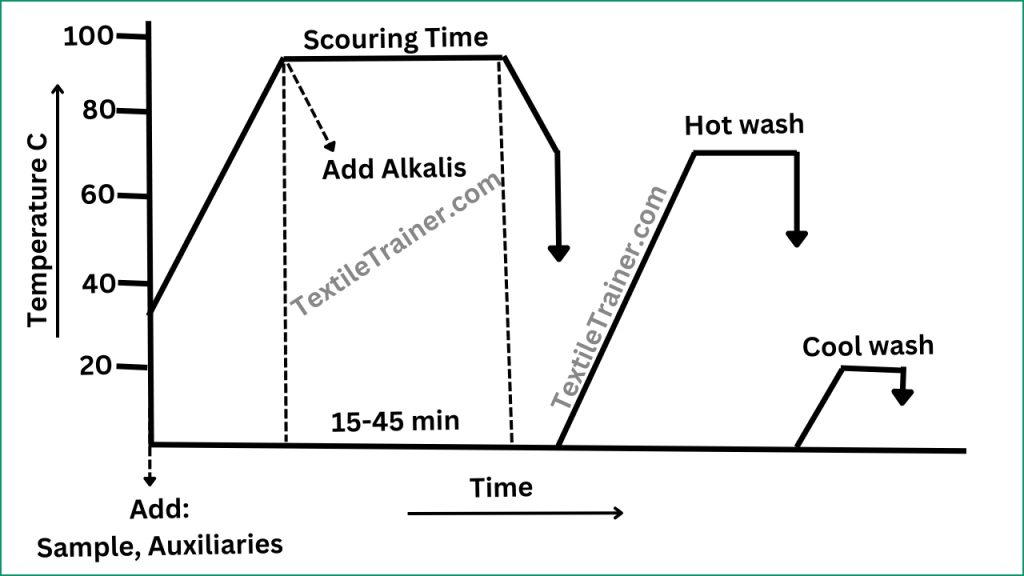
Working Procedure of Scouring of Cotton
- At first, additional water, wetting agent, sequestering agent and detergent is add at room temperature.
- After 2-3 minute, raise the temperature to 95-1000C and add alkalis (Caustic soda)
- Run the bath for 15-45 min.
- After 45 min, cool down the bath temperature to 70-800 C and drop.
- Now, rinse the sample twice with hot and cold water.
- Finally, neutralize with acetic acid.
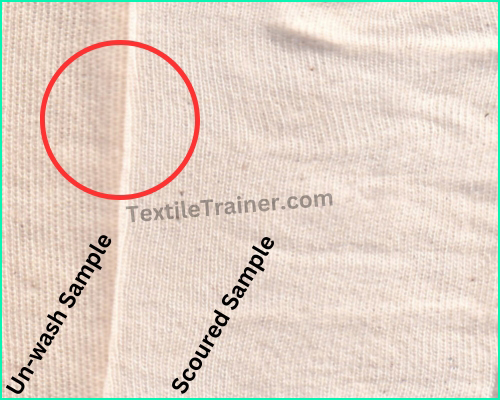
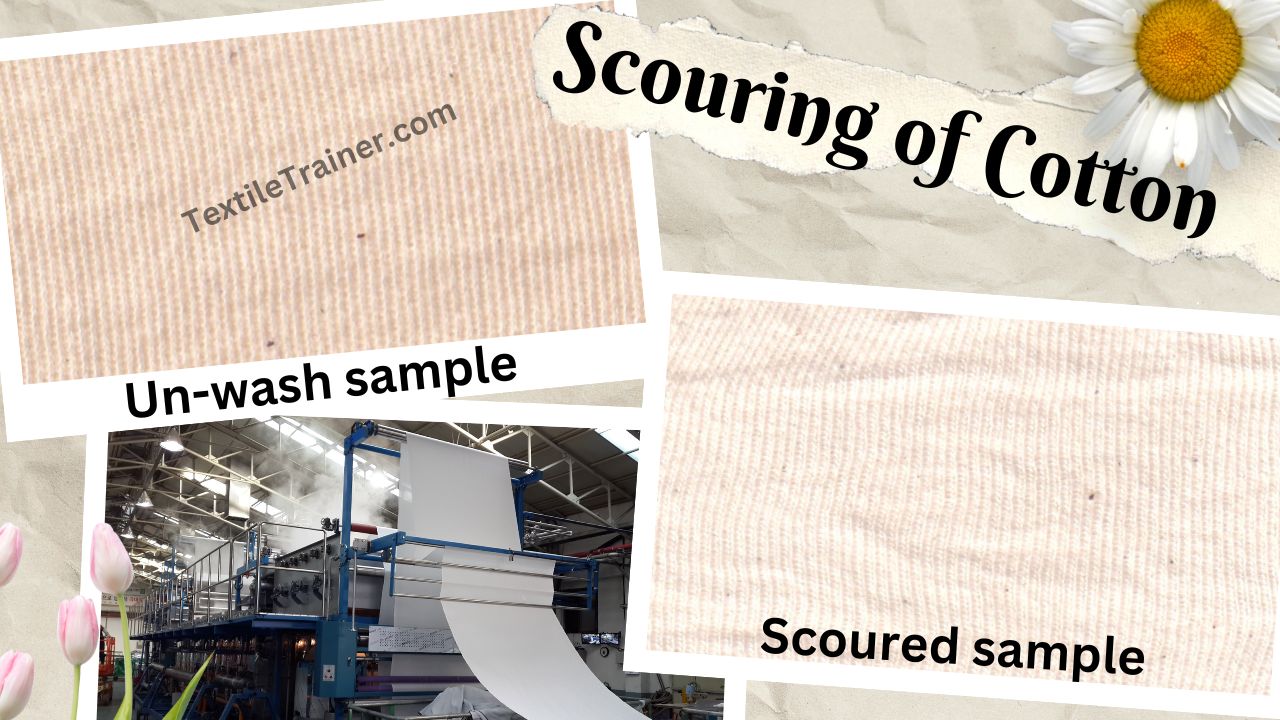
Result:


Precaution:
- Ensure all equipment are clean and free from contamination.
- Wear safety gloves, goggles and protective cloth.
- Follow the chemical manufacturer’s guideline.
- Proper maintain temperature and pH.
Conclusion:
In textile wet processing, scouring plays a vital role, particularly with cotton fibers. Fabrics are prepared for dyeing and finishing after they have been carefully cleaned of impurities, natural waxes, and oils. Manufacturers can ensure that the scouring process is effective, safe, and sustainable by implementing a comprehensive set of precautions.
You may read:
- cotton-polyester blended dyeing process.
- History of wool with geographical distribution.
- Classification of wool fiber.
- Morphology of wool fiber.
- Woolen Vs Worsted Fabric.
- Wool Manufacturing Process.
- Physical Properties of wool.
Reference:
- Belal, P. D. (2016). Understanding Textiles for a Merchandiser. Dhaka: LB Graphics & Printing.
- Hossain, M. F. (2015). Practice of Textile Coloration, Volume-I. Dhaka: Books Fair Publications.
- Hossain, M. S. (2014). Introduction to Textile Engineering. Dhaka: Books Fair Publications.
- Kabir, D. S. (2016). Chemistry of Dyes & Pigments. Dhaka: Books Fair Publications.






4 thoughts on “Study on Scouring of Cotton Fabric with Easy Recipe Calculation/Lab Report-2”