Name of the Experiment:
Study on dyeing process of jute fabric with basic dye./Study on jute fabric dyeing with basic dye and calculate basic dye recipe.
Introduction:
Jute fibers are mainly used for making packaging materials, and a small quantity is used for producing diversified value-added products like curtains, upholstery, soft luggage, fancy dress materials, cables, carpet backing, wall coverings, coated textiles, automotive textiles, reinforced composite materials etc. It is a bast fiber composed of cellulose (62-65%), hemicellulose (22%), lignin (11.8%), oil and wax (0.4%), Ashes (0.7%) and coloring matters. It is necessary to incorporate small amounts of mineral spindle oils into the fiber during conversion into yarn. These impurities are mainly responsible for creating different problems during the processing of jute fibers. In the pretreatment process, most of these impurities are removed before dyeing. The main difference is that pretreatment of jute fibers requires less caustic soda than cotton treatment.
Jute dyeing can also be done with dyes that are appropriate for cotton. In practice, jute dyeing with these dyes, however, has some limitations. This fiber has a special affinity for basic dyestuffs, so brilliant shades can be achieved even on unbleached jute. These shades are fast in light and water, but they are also dull at a reasonable cost. Acid, direct and sulfur dyes are increasingly fast in this order, but give increasingly dull shades. Very bright and fast results are obtained with azoic and vat dyes, but their high cost confines this application.
Objectives:
- To know about jute fiber.
- To know how to dyeing jute fabric with basic dyes.
- Come to learn recipe calculation of jute fabric dyeing.
- To know working procedure of jute fabric dyeing process with basic dyes.
Typical recipe for Jute Fabric dyeing:
| Chemical | Amount (gm/l) |
| Wetting agent | 0.5-1.0 gm/l |
| Sequestering agent | 1.0-2.0 gm/l |
| Dyes (Yellow) | 1.5% |
| Dyes (Blue) | 0.5% |
| Glauber salt | 10-20 gm/l |
| Acetic acid | 1.0-3.0 gm/l(to maintain pH 4-5) |
| Temperature | 80-1000C |
| Time | 30-50 min |
| M:L | 1:20 |
| Sample weight | 10 gm |
Recipe Calculation:
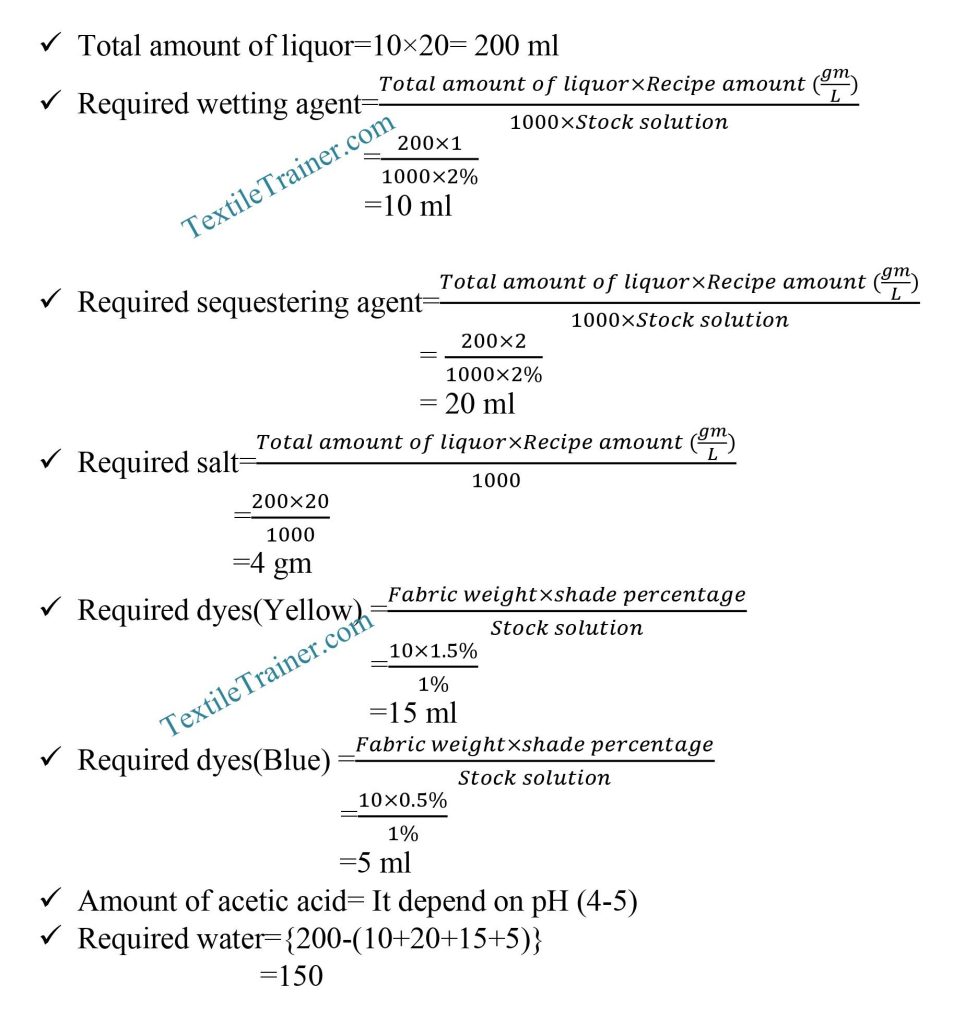
Dye Solution Preparation:
We know, basic mainly water soluble and catanionic dye. But application, it is better to make dye paste. At first, we will take 100 ml hot water, add little amount of wetting agent and acetic acid with the hot water. Now, we weight 1 gm dyestuff. Then add in hot water and stir it to make desirable dye solution.
Process Curve:
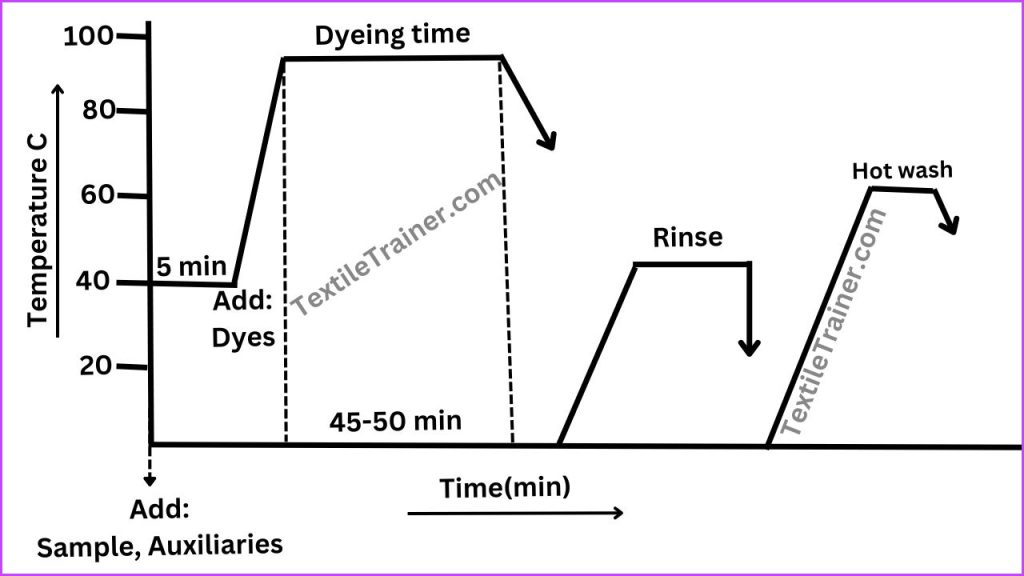
Working procedure:
- Set the dye bath with sample at room temperature.
- Now, add required dyes solution into the dye bath with salt, acid and other chemicals auxiliaries.
- Run the bath for 15-30 min at the same temperature.
- Then raise the temperature to 80-850C over 15-25 min. Rate of temperature raise should 1-30C/min.
- Run the dye bath at 80-850C for 30-45 min.
- Now, cool down the bath temperature to 60-700C.
- Drop the dye bath liquor and carry on the after treatment process.
- To improve colorfastness properties, sample should be successive hot and cold wash to remove unfixed dyes from the surface of jute fabric.
Result:
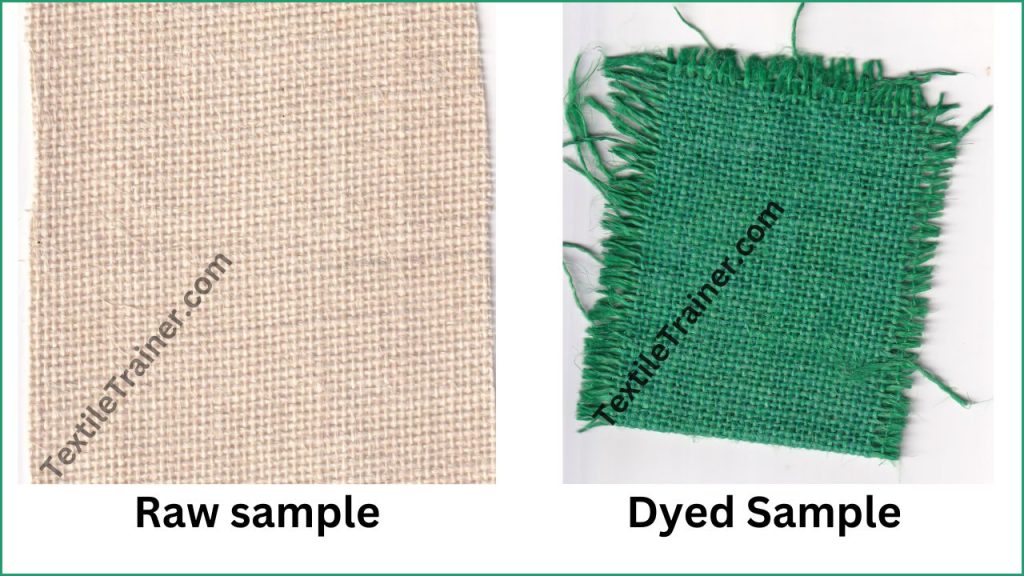

Conclusion:
I learned a lot from this experiment, regarding the dyeing process of jute fabric with basic dye. Thanks to our teacher for helping us to carry out this experiment. I think this experiment will be useful to me in my future career.
More lab report:






I really liked your blog.Thanks Again. Awesome.