Reactive Dyes on Cotton Fabric with Easy Recipe Calculation
Name of the Experiment :
Study on reactive dyes on cotton fabric.
Introduction:
The use of reactive dyes for textile coloration has become increasingly popular due to their specific properties such as colorfastness, wide shade range, brilliance, reproducibility, and ease of application. In the presence of alkali, reactive dye reacts with fibers and adheres to them as part of the fibers. There are three basic steps involved in reactive dyeing: exhaustion, fixation or reaction, and washing. The negative charge produced by a cellulosic fiber is surrounded by a dye solution when it is immersed in the dye solution.
In contrast, reactive dyes produce negative charges that are deposited into the dye-bath, so a repulsion force occurs. Electrolytes neutralize the negative surface charge. Adsorption occurs during dyeing, when the dye molecules move forward to the fiber surface because of their affinity for the fiber. In the next step, the dye molecules diffuse into swollen fiber pores and spread throughout the fiber – this is called exhaustion. By forming a strong covalent bond with cellulose, the dye molecules affixed to the fiber – this process is called fixation. Following this, the loosely attached and unfixed hydrolyzed dyes are removed by successive soap, hot, and cold washings; which ensures a better shade and fastness in the reactive dyeing process.
Objectives:
- To know about reactive dyes properties.
- Come to learn dyeing parameter of reactive dyes.
- To know dyeing process of reactive dyes on cotton fabric.
Major reactive dye types:
Following types of reactive dyes are used in factory. They are:
- Cold brand dyes.
- Hot brand dyes.
- High exhaust dyes.
- Vinyl sulphone dyes.
- Bi-functional dyes.
In this experiment, we will use hot brand reactive dyes. It is very common to use these dyes for medium to heavy fabrics since they have good migration and penetration properties. A higher temperature of about 90°C is used to apply these dyes to textiles. Addition of salt and alkalis is necessary for the exhaustion and fixation of dyes into fibers. In order to achieve best results, salt should be added step by step, followed by alkalis after the dyes have been exhausted into the fibers. Most dyestuffs manufacturers recommend the amount of salt, alkalis, and other auxiliaries used in dye-baths depending on the depth of shade.
Typical recipe for Reactive Dyes on Cotton:
| Chemical | Amount (gm/l) |
| Wetting agent | 0.2-0.5 gm/l |
| Sequestering agent | 1.0-2.0 gm/l |
| Antifoaming agent | 0.5-1.0 gm/l |
| Dyes | 3% |
| Glauber salt | 40-60 gm/l |
| Soda ash | 10-15 gm/l |
| Lubricating agent | 1.0-2.0 gm/l |
| Temperature | 95±50 C |
| Time | 30-60 min |
| pH | 10.5±0.5 |
| M:L | 1:20 |
| Sample weight | 5 gm |
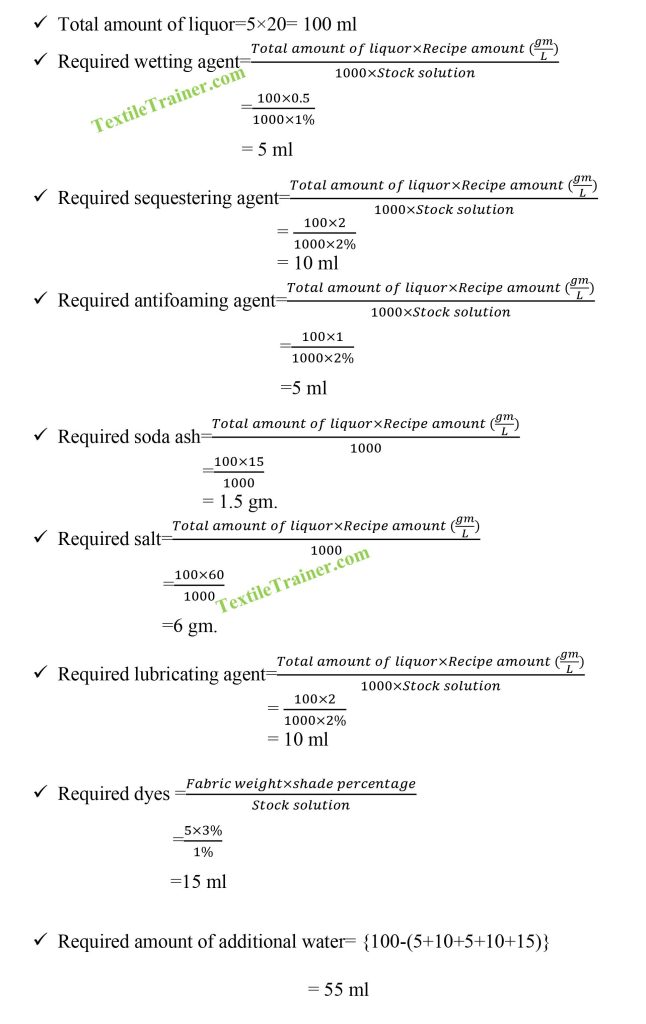
Recipe Calculation:
Process Curve:

Working procedure:
- Set the dye bath with sample and add wetting agent, sequestering agent, lubricant, anti-foaming agent at room temperature.
- Add dyes and glauber salt (1st dosing) at 400 C.
- Raise the temperature to 95-1000 C and add soda ash, glauber salt (2nd dosing).
- Run the dye bath for 30-60 min at dyeing temperature.
- Cool down the bath to 600 C and drop the liquor.
- Carry on after treatment process.
After treatment process:
To improve colorfastness properties after treatment process is very important. At first need to remove the salt and alkalis by rinsing. Then the sample is neutralized by acid. After that, sample is wash by following process:
Recipe for after treatment:
| Chemical | Amount (gm/l) |
| Detergent | 1.0-3.0 gm/l |
| Soda ash | 0.5-1.0 gm/l |
| Temperature | 95-1000 C |
| Time | 15 min |
| pH | 8-9 |
| M:L | With enough water. |
- At first rinse the sample with hot water for 10 min.
- Then sample is neutralized with acid at 500C.
- Now soap wash is carry on according to the mentioned above recipe.
- Then rinse the sample with hot water for 10 min.
- Finally cold wash the sample.
Result:


Precaution:
- Since dye hydrolysis occurs during preparation, dye solutions cannot be stored for later use.
- An inhalation of reactive dye dust can be dangerous, so a protective mask is recommended.
- Most reactive dyes have a limited storage period.
Conclusion:
There are many reasons why reactive dyes are so popular for textile coloration, such as their excellent colorfastness. Through this experiment, we were able to learn more about reactive dyeing methods with cotton fabrics. We are thankful to our teacher for assisting us in this experiment.
More Lab Report: