The reduction of entangled mass of fibers of filmy web by working them between two closely spaced relatively moving surface closed with sharp points is called carding. It is the preliminary process in spun yarn technology just after the blow-room process. Card is the heart of spinning mill and well carded is half spun.
Action of carding machine:
Carding machine operates by performing several actions. Some important actions are discussed below.
1. Stripping Action:
when the wire points of two closed surface are inclined to the same direction and both the surfaces rotate to the opposite direction then the action is called stripping action.
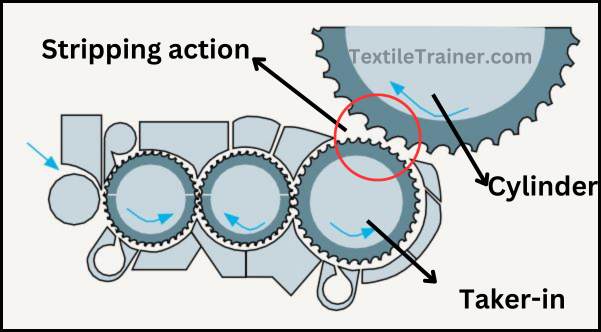
This type of action arrangement is used for intensive opening. This system is observed usually in blow room and pre-opening zone of card frame. Small tufts attached to the sharp points of delivery roller rotating in the opposite direction at a higher surface speed of the delivery beater. Travelling direction of fiber is from slower beater to faster beater. The “front of the tooth” of the faster roller works on the “Back of the tooth” of the slower beater and will “strip” the tufts from the latter, slower moving surface. This principle of point’s actin is defined as “point-of-tooth to back-of-tooth” and gives a stripping action. This type of action is held between taker-in to cylinder.
2. Carding Action:
when wire points of two closed surface are inclined to the opposite direction and fiber tuft weight is reduced by the relative motion of the two surfaces then the action is called carding action.
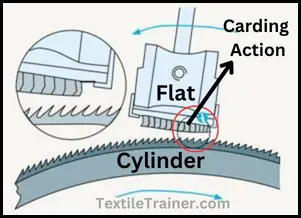
This type of action arrangement is used for achieving the degree of signalization by very intensive opening. This system is observed usually is card frame. To disentangle the fibers of the tufts to individual fiber, the tufts attached to the faster-moving surface need sharp points clothed stationary or much slower moving surface and is required to be in close proximity with the faster surface. The motion of the slower surface may be in the same or opposing direction, but the sharp points will be angled to oppose those of the faster moving surface. Travelling direction of fiber is along to fastest beater. The “front-of-tooth” of the fastest roller work on the “front-of-tooth” of the slower moving or stationary surface and will “card” the tufts between the fastest and slower moving surface. The principle of point’s action is defined as Point-of-tooth to point-of-tooth and gives the carding action. This type of action is held between cylinder and flat.
3. Doffing Action:
When the wire points of two closed surface are inclined to the opposite direction and both the surfaces rotate to the same direction then the action is called doffing action.
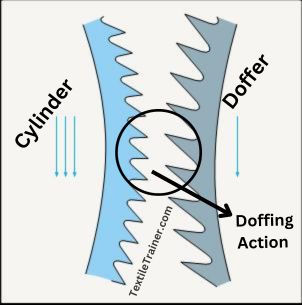
This type of action arrangement is used for achieving the building a web of individual fibers by transferring the fibers to a slower moving surface. To transfer the fibers, the fibers belonging to the faster-moving surface need much slower moving surface and higher carding angled points and very close spacing between the faster moving and much slower moving surface for having of higher degree of captivity to the delivery end. The motion of the slower surface should be in the same direction, but the sharp points will be angled at greater degree to oppose those of the faster moving surface. Travelling direction of fiber is from faster roller to slower roller. The “front-of-tooth” of the slower roller work on the “front-of-tooth” of the fastest roller and will “transfer” the single fibers from the fastest roll to slower moving surface. This principle of point’s action is defined as “point-of-tooth” to “point-of-tooth” and gives the stripping action. This action held between cylinder and doffer.
4. Combing Action:
The main work of this zone is opening of compact and large fiber package to micro tufts. As the fiber mass held by the feed roller is opened by the taker-in wire, by the combination of nipping of feed roller to point-of-tooth taker-in, combing action takes. This action is held between feed roller and taker-in.
Differences Between Carding and Stripping Action:
| S/N | Carding action | Stripping action |
| 01. | The wire points on two surfaces are inclined in opposite directions. | The wire points on two surfaces are inclined in the same direction. |
| 02. | The direction of their speed is opposite | The direction of their speed is the same. |
| 03. | It occurs between flats and cylinders | It occurs between cylinder and Taker-in |
| 04. | Fiber stays in lower speedy surface since two surfaces are in opposite directions in this action. | In this action, both surfaces are in the same direction, so maximum fibers remain on the lower, speedier surface. |
| 05. | Point to action | Point to back action |
Differences Between Carding and Doffing Action:
| S/N | Carding Action | Doffing Action |
| 01. | The wire points on two surfaces are inclined in opposite directions, and their speed direction is also opposite. | The wire points on two surfaces are inclined in opposite directions, but their speed direction is the same. |
| 02. | It occurs between flats and cylinders | It occurs between the cylinder and the doffer. |
| 03. | There is a greater speed difference between two surfaces. | There is a smaller speed difference between two surfaces. |
| 04. | This action mainly individualizes fibers. | This action results in the formation of slivers. |
You May Read:
- Objectives and basic function of carding machine.
- Working principle of carding machine.
- Why carding is called heart of spinning?
- Operating zone of carding machine.
- Neps in carding machine.
- Function of carding machine.
- Types of card clothing with advantage and disadvantage.
- Flexible card clothing vs metallic card clothing.
Reference:
- Chowdhury, M. F. (2016). Manual of short staple spinning. Dhaka: Granthanir Prokashoni.
- Hossain, M. S. (2014). Introduction to Textile Engineering. Dhaka: Books Fair Publications.
- Kadolph, S. J. (2006). Textiles. New Delhi: Pearson Education.
- Prof. Dr. Engr. Ayub Nabi Khan, E. M. (2088). Principles of short staple spinning. Dhaka: Books Fair.





Saved as a favorite, I really like your blog!
There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made