Introduction:
Carding machine is heart of spinning mill. In this article, I will describe operating zone of carding machine. Through the use of cards, tangled fibers can be reduced in size to individual fibers and formed into a filmy web by working the tufts between two surfaces that are closely spaced and have opposing sharp points. This work is performed by machines known as cards. It is the most effective method of opening tufts of a few milligrams produced during opening and cleaning into very small, well opened tufts containing almost single fibers through carding.
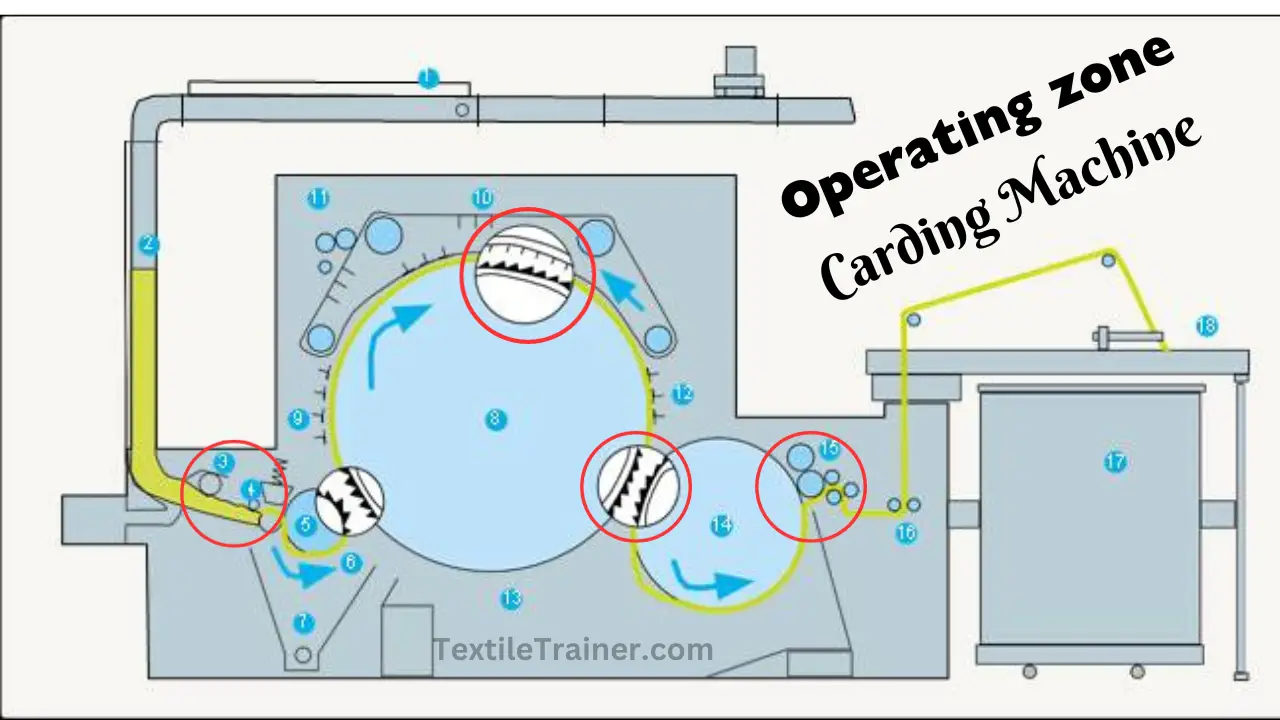
Operating Zone of Carding Machine:
1. Feed Zone: (Chute Device to Feed Roller)
This consists of feed arrangement, card mat opening roll and chute assembly. In the feed roller-taker-in zone, materials are stored, opened and cleaned to prepare them for intensive combing. The feed zone comprises the lap stand, lap roller, and feed roller in conventional card frames.
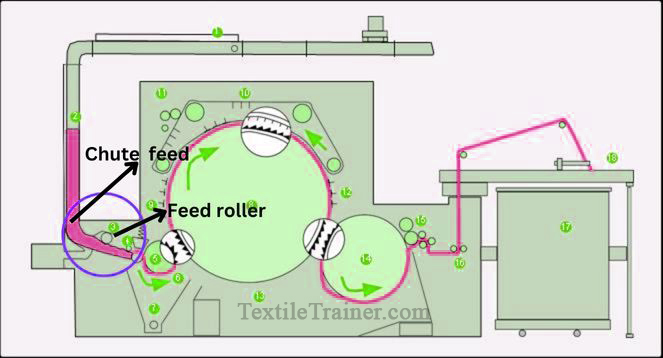
Function of feed zone:
- Ensure that the fiber tuft is clamped tightly over its entire width.
- Maintain the proper tension of the card feed material to prevent breakage or deterioration of quality.
- To feed the material in such a way as to withstand the intensive combing action in the feed roller-taker-in zone.
- This is to make sure that the tuft is presented to the taker-in in such a way that he or she can carry out a gentle opening.
2. Pre-opening Zone: (Feed Roller to taker-in)
This zone comprises a feed roller and spring loaded feed plate, beaters known as takers, and a motel knife for cleaning. As a result of intensive combing, 30% of the tufts are opened to single fiber in this zone, while the rest pass to the cylinder as tuftlets and microtuftlets.
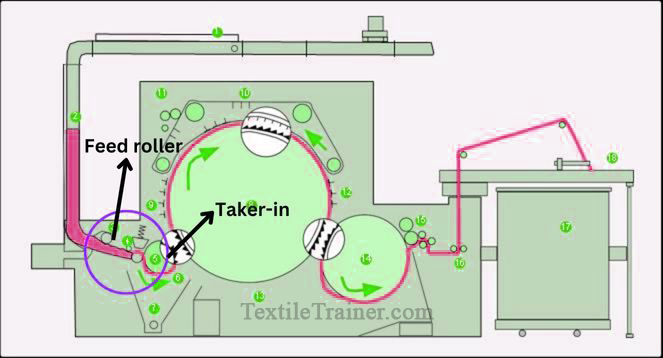
Function of pre-opening zone:
- In order to feed the material in a controlled tension to the taker-in.
- To remove impurities.
- In order to perform the intensive cleaning and opening of cotton fibers.
3. Pre-transfer zone: (Taker-in to cylinder)
The taker-in and the cylinder are in this zone, where fibers are transferred from the taker-in to the cylinder through the clothing arrangement back-of-tooth (taker-in) to point-of-tooth (cylinder). Between the taker-in and the cylinder clothing, a back-of-tooth (taker-in) to point-of-tooth (cylinder) doffing action occurs as the fiber mass on the taker-in clothing is taken up by the cylinder wire. Fiber is treated gently in this zone, and approximately draft 2 is maintained between these two carding rollers.
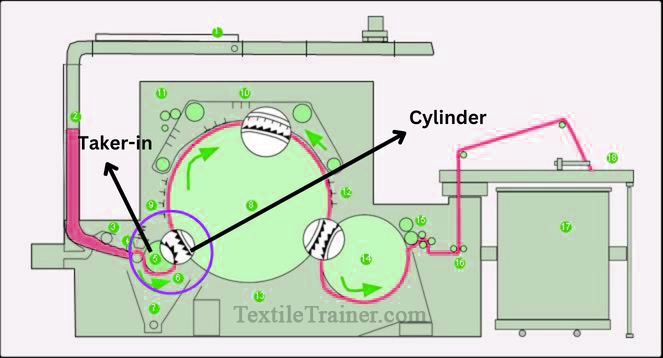
Function of pre-transfer zone:
- To feed the material into the cylinder in a controlled stretch.
- To remove impurities.
- to transfer the material as evenly as possible.
- Performing the primary cleaning and opening of cotton fibers.
4. Carding zone: (Cylinder to flat)
There are cylinders, revolving flats and fixed flats in this zone, which is the primary operating area. By arranging fibers from point-of-tooth (flat) to point-of-tooth (cylinder), the fibers are opened to single fibers in this zone. Between the main cylinder and work-in flats, the card opens to individual fibers.
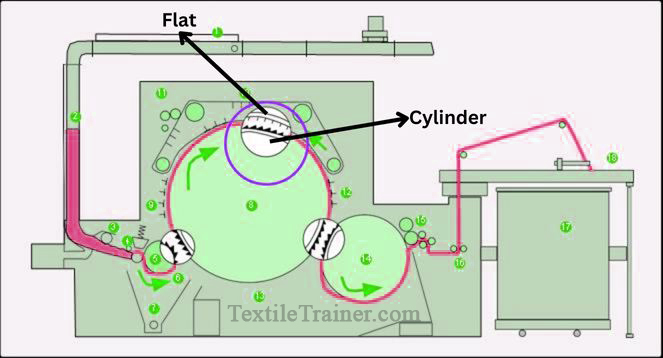
Function of carding zone:
- The fibers are opened gently here. The fibers are singled, i.e. the tufts are opened to individual fibers.
- There is also the task of unnepping in the cylinder-flat zone, where neps are opened out and reduced.
- In this zone, the fibers are also cleaned. The fibers are cleaned optimally in this zone.
5. Post Transfer Zone: (Cylinder to doffer)
There are two parts to this zone: a cylinder and doffer. Despite the fact that the clothing arrangement follows a point-of-tooth pattern, fiber transfer occurs here at a slower rate. As the individual fibers attach to the cylinder clothing, they collectively form a very light web on the cylinder surface. In this zone, fiber mass transfer, doffer web formation and consolidation take place. Through the point-of-tooth to point-of-width stripping action, the web contacts the doffer clothing, which removes the fibers from the cylinder. This area of the cylinder-doffer is called the transfer zone.
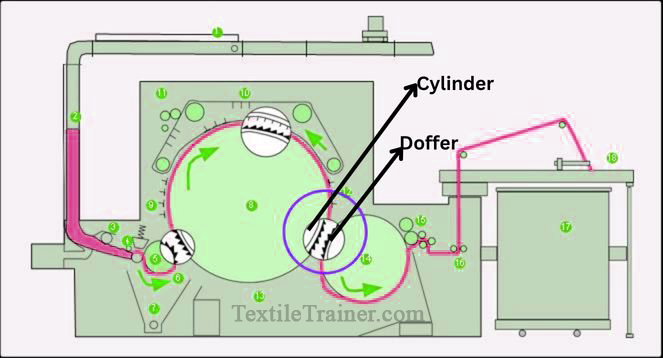
Function of post transfer zone:
- Fibers are transferred from the cylinder surface to the doffer surface.
- To form a continuous web from the collected fibers in the form of doffer webs.
6. Condensation & Consolidation zone: (Sliver formation)
Basically, this zone consists of stripping rollers, crushing rollers, condenser and calendar rollers, coiler calendar rolls, coiling mechanism, sliver cans and can changer assemblies. In this zone, the first intermediate product i.e. a sliver can can be produced which can be transported.
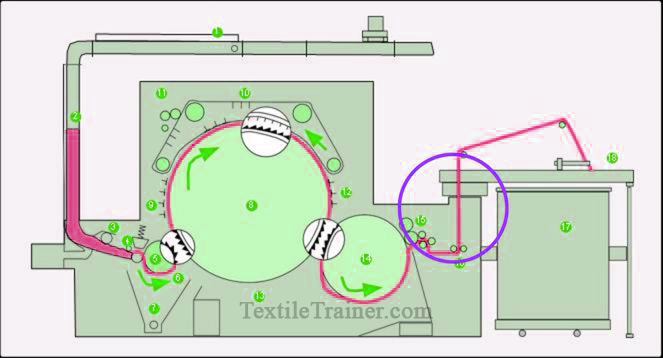
Function of condensation & consolidation zone:
- By using a doffer comb or stripping roller, the fiber is collected from the doffer surface.
- Through the use of calendar rollers and trumpeting devices, fibers are condensed into continuous rope forms known as sliver.
- Using the coiling mechanism, the sliver is deposited into the can as coils.
- Crushing rollers are used for cleaning large trash particles.
You may read:





3 thoughts on “Essential 6 Operating Zone of Carding Machine with Dynamic Function”