Experiment Name:
Lab Report: Study on main parts, functions and yarn passage diagram of circular knitting machine.
Introduction:
As the name implies, knitting is the process of converting yarn into fabric by interloping it with needles. The weft knitting technique is a way of forming knitted fabrics with loops created horizontally from a single yarn and interloping that occurs crosswise in a circular or flat form. Knitting consists of three basic elements are:
- Needle
- Sinker
- Cam
In this experiment, we will learn yarn passage diagram of circular knitting machine and it parts name with function. All parts of a circular knitting machine play an important role in ensuring that the machine runs smoothly. Every piece of a circular knitting machine has a specific function.
Objectives:
- To know about the single jersey circular knitting machine.
- To know about the main parts of the circular knitting machine.
- To know about the functions of the main parts of the circular knitting machine.
- To observe the yarn passage path in operation of the circular knitting machine.
- To draw a yarn passage diagram of circular knitting machine.
- To make a report on the experimental work.
Working Procedure:
- Observe the knitting production of a circular knitting machine with an inching motion at first.
- Then become familiar with the main components and functions of knitting machines.
- Lastly, draw a clear diagram of the yarn passage of a circular knitting machine.
Diagram of Circular Knitting Machine:
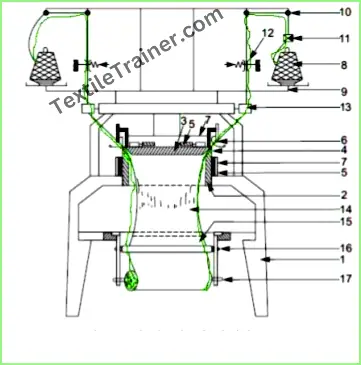
Main Parts and Function of Circular Knitting Machine:
- Creel: A creel is part of a knitting machine, where yarn packages are stored and ready for feeding.
- VDQ Pulley: In the machine, it is a very important part. Altering the tension pulley’s position changes the fabric’s GSM. If the pulley moves towards a positive direction, the fabric’s GSM will decrease. When the pulley moves in the opposite direction, the fabric’s GSM will increase.
- Pulley Belt: Rotation of the MPF wheel is controlled by this device.
- Brush: It’s a clean pulley belt.
- Tension Disk: In addition, it confronts the tension of the supply yarn.
- Inlet and Outlet Stop Motion: It is an important part of the machine. It stop the machine immediately when a yarn breaks.
- Yarn Guide: It helps the yarn feed into the feeder.
- MPF Wheel: This is what controls the speed of the MPF. A pulley belt is attached to the wheel in order to give it motion.
- MPF: Mamenger positive feed is another important part of the machine. It provides positive feed to the machine.
- Feeder Ring: In a ring, all feeders are pleased with each other.
- Feeder: Yarn is fed into the machine through a feeder.
- Needle Track: All Needles are arranged in a decent manner.
- Needle: Using it, the yarn creates a loop. By doing this, fabric is made. Prior to yarn feeding, the needle is raised to clear the old loop from the hook and is then received above it on the needle stem with the new loop. Once the needle begins to descend, the new loop is encased in the needle hook.
- Sinker: This is the most important component of the machine. It aids in loop formation, knocking over and holding down the loop.
- Sinker Ring: Sinker rings are rings where sinkers are placed together.
- Cam Box: This is where the cams are horizontally positioned.
- Cam: The cam converts the rotary machine drive into a reciprocating action for the needles and other elements.
- Lycra Attachment Device: We place the Lycra here and feed it to the machine.
- Lycra Stop Motion: A stop motion is used when the Lycra breaks to stop the machine.
- Cylinder: The needle track is located here.
- Cylinder Balancer: In this way, a proper alignment of the cylinder can be achieved.
- Uniwave© Lubrication: The Uniwave© lubricator ensures uniform lubrication of needles, cam tracks, lifters, and other knitting machine components. The patented nozzle construction separates air and oil droplets.
- Adjustable Fan: The purpose of this part is to clean the dust by air flow by removing lint, hairy fibers from yarn, and others.
- Expander: The fabric width can be controlled. There is no distortion of the knitting courses. The tension in the knitting machine can be evened out. As a result, a uniform fabric structure is achieved over the entire width of the fabric.
- Needle Detector: The part detects any type of needle fault.
- Air Gun Nozzle: Sometimes it is used for cleaning as well as feeding the yarn.
Conclusion:
We learned about circular knitting machines from this experiment. We also learned the parts and their functions. This experiment will help us in our future lives. Thanks to our teacher for his assistance.
You May Read:
- Effective Layout Plan of Fabric Engineering Lab.
- Basic Principle of Weaving: Very Easy Way.
- Yarn Passage Diagram of Pirn Winding Machine is Described Easy Way.
- Dynamic Layout Plan of Spinning Lab.
- Bale Breaker Material Passage Diagram: Easy Description.
- Step Cleaner Machine: Simple Working Principle.
- Hopper Feeder Machine in Blow Room with Simple Working Principle.
- Porcupine Opener Machine in Blow Room: Simple Working Principle.
- Scutcher Machine in Blow Room: Feed to Carding Effective Way.
- Material Passage Diagram of Carding Machine with Easy Description.
- Material Passage Diagram of Lap Former Machine.
- Working Principle of Comber Machine: Better Quality Yarn.
- Working Principle of Speed Frame in Ring Spinning with Simple Description.
- Ring Spinning Frame: Working Principle is Describe Very Easy Way.
- Easy Way: Autoconer in spinning working Principle.






1 thought on “Yarn Passage Diagram of Circular Knitting Machine/ Lab Report -08”